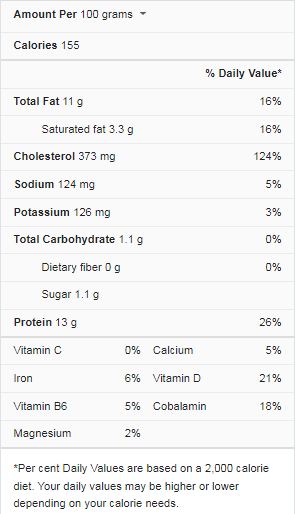
In this article, you will get all the important information about Eggland’s Best Extra Large Eggs Nutrition Facts. Besides being delicious, Eggland’s Best extra-large eggs are also nutritionally enhanced. They contain 125 mg of omega-three fatty acids and 25 percent less saturated fat than standard eggs. What’s more, these delicious eggs stay fresh longer! Moreover, the company even takes egg nutrition seriously, so the product has a nutrition label explaining every nutrient.
The hens that produce Eggland’s Best eggs are fed a proprietary vegetarian diet. The result is a higher-quality egg that contains more vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids than ordinary eggs. The nutrients are packed into a single large egg, and they have nearly half the saturated fat of regular eggs. The hens are also raised on a vegan diet, which helps the eggs stay fresher. And the taste is a big plus – consumers have given them top marks in Men’s Health, Women’s Health, and Prevention.
Nutrition Facts of Eggland’s Best Extra Large Eggs:
Here are Eggland’s Best Extra Large Eggs Nutrition Facts:
Types Of Eggland’s Eggs
- Organic Eggs
- Cage-Free Eggs
- Classic Eggs
- Hard-Cooked Peeled Eggs
Eggland’s Best extra-large eggs are a great source of vitamin nutrition. Compared to ordinary eggs, they contain twenty-five percent less saturated fat and four times as much vitamin D. What’s more, they contain twenty-five percent less saturated fatty acids than ordinary eggs. And because the hens are vegetarian-fed, they are healthier, more delicious, and fresher for longer.
Organic Eggs
The laying hens are fed all-organic feed with no animal byproducts or antibiotics to produce organic eggs. Organic farms also adhere to stricter animal welfare guidelines. Eggland’s Best organic eggs bear the USDA’s official seal of approval, indicating that they have been certified.
Cage-Free Eggs
Cage-free eggs in brown and white variants are available from Eggland’s Best. Their cage-free hens also offer a healthful, all-vegetarian diet free of recycled or processed foods to ensure nutritional superiority. Eggland’s Best cage-free eggs are available in 100 percent recyclable plastic cartons at your local supermarket.
Classic Eggs
- Egg Whites
- Brown Egg
Eggs of varied kinds are available at most grocery and convenience stores. Eggland’s Best is a superior alternative to regular eggs, with more nutritional value, less saturated fat, and fewer calories. EB eggs have ten times the amount of vitamin E, more than double the omega-3s, more than twice the amount of vitamin B, and six times the amount of vitamin D as regular eggs.
They are choosing Eggland’s eggs, whether organic, cage-free or traditional, as a simple way to add additional nutrients and freshness to family meals. You can make a better-informed selection while shopping at your local grocery store and guarantee that you bring home the correct carton for you and your family if you grasp the essential distinctions between eggs.
Egg Whites
The clear liquid, also known as albumen or glair-contained within an egg, is egg white. It comprises layers of secretions from the hen’s oviduct’s anterior part during the egg’s passage in chickens. It forms around the yolks of fertilized or unfertilized eggs.
When an egg is fertilized, the egg white’s principal function is to protect the yolk and give more nutrition for the embryo’s growth. Most of an egg white is made up of water, with roughly 10% of the protein dissolved.
Unlike the yolk, which is heavy in lipids and fats, egg white has no fat and less than 1% carbohydrate content. About 56% of the protein in an egg is found in the whites. Egg white has a wide range of culinary and non-culinary applications.
Brown Egg
Brown eggs are giant and darker than their white counterparts. In addition, the brown egg originates from a bird with a voracious appetite. The difference in nutrition: Both have the same amount of calories. However, the overall nutritional content of the eggs is determined by the chicken’s surroundings.
Hard-Cooked Peeled Eggs
The varying rates at which aluminum, stainless steel, and cast iron bring water to a boil and maintain heat are well known.
So, if your eggs are sitting in a pot of cold water in a cast iron pot that takes two minutes longer to get to a boil than an aluminum pot (not to mention the water cools at a far slower rate once withdrawn from the heat), you’ve now accidentally cooked your eggs for a few minutes longer.
Although this isn’t the end of the world for hard-boiled eggs, it does raise the chances of a green tinge around the yolk and a rubbery white. In other words, hard-cooked eggs aren’t entirely flawless.
Is Eggland Best Better For You?
According to the company’s ads, Eggland’s Best eggs not only “taste better,” but they’re also healthier, with more nutrition and vitamins than “regular eggs.” According to Eggland’s Best, their eggs have more vitamins and less saturated and total fat than regular eggs.
Why Should You Avoid Buying Brown Wiggs?
Brown egg breeds are supposed to be more antagonistic to one another. It also sounds like hostility isn’t natural to the brown-egg layers, at the risk of being overly emotional. Thus they are debeaked using an infrared amputation procedure that is thought to be extremely painful.
What Are Some Of The Advantages Of Brown Eggs?
The color of the shell influences people’s choices of eggs, and some believe brown eggs are superior or healthier. Brown and white eggs, on the other hand, have no discernible nutritional differences.
Which Egg Is The Most Nutritious?
Omega-3-enriched eggs and eggs from pasture-raised hens are the best options. Omega-3s and essential fat-soluble vitamins are substantially greater in these eggs (44, 45).
Which Egg Contains The Most Protein?
A large egg has six grams of protein, and the egg white is the most protein-dense portion of the egg, containing more than half of the total protein content at roughly 3.6 grams. However, at 2.7 grams of protein, the yolk still packs a punch.
Which Egg Is Best For Losing Weight?
Eggs are a great source of protein and are sometimes referred to as the “nutritional powerhouse.” Eggs are your best bet if you’re attempting to reduce weight or gain muscle because they’re packed with all of the essential nutrients.
On the other hand, Egg yolk has long been a source of contention. It is unhealthy because it has excessive cholesterol related to cardiac problems. Additionally, folks who want a flat stomach and six-pack abs eat only egg whites and skip the yolks. Should you avoid eating egg yolk if you’re trying to lose weight?
Conclusion
The nutritional benefits of England’s best extra-large eggs are outstanding. They contain 40% less saturated fat, four times the vitamin D, and half the omega-3 fatty acids of regular eggs. They also have up to 50% less fat than average-sized eggs. And despite their high-calorie content, they are still an excellent source of vitamin D, vitamin E, and Omega-3. This is an excellent source of iron, a key component in a balanced diet.