Mushrooms are versatile and flavorful ingredients that can be used in a variety of dishes. They are also high in essential nutrients and have been linked to a variety of health benefits. We will look at the nutrition facts of mushrooms in this article, including their calorie content, macronutrient profile, and micronutrient content. We will also look into the potential health benefits of mushrooms, such as their effects on the immune system, cancer risk, and other factors.
Whether you’re a mushroom lover or just trying to diversify your diet, this article will provide you with all the information you need to incorporate mushrooms into your meals.
What are Mushrooms?
Mushrooms are a form of fungus that can grow on the ground, on trees, and within other plants. They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors, and can be found in both their natural and domesticated forms.
Mushrooms are nutritionally dense, low in calories and fat, and a superb source of protein, fiber, and other necessary vitamins and minerals. In addition, they contain antioxidants, which can protect cells from harm caused by free radicals.
Mushrooms can be consumed raw or cooked and are utilized in numerous cuisines, including soups, stews, salads, pizzas, and sandwiches. They are also popular among vegetarians and vegans as a substitute for meat.
Mushrooms have been used in traditional medicine to prevent and treat a range of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
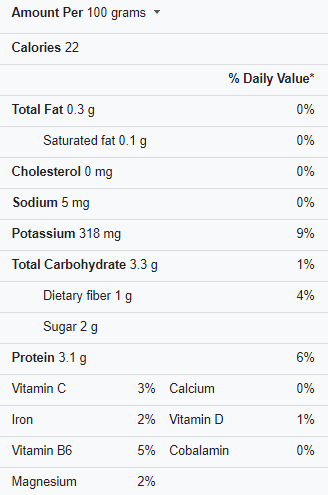
Mushroom Nutrition Facts
Mushrooms are low in calories and fat, and they provide a variety of essential nutrients. A 100-gram serving of mushrooms contains the following nutrients:
- 22 calories
- 3 grams of protein
- 0.2 grams of fat
- 3 grams of carbohydrates
- 2 grams of dietary fiber
- 0.1 grams of sugar
Mushrooms are also high in a variety of vitamins and minerals, including:
- Mushrooms are one of the few food sources of vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and immune system function.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): essential for energy production and overall health.
- Niacin (vitamin B3) is essential for the skin, nerves, and digestion.
- Copper is necessary for the formation of red blood cells as well as the immune system.
- Selenium is essential for thyroid and immune system function.
- Potassium is essential for maintaining normal blood pressure.
Mushrooms are also high in antioxidants and have been linked to a variety of health benefits such as improved immune function, lower cancer risk, and better gut health.
It is important to note that some mushrooms, such as shiitake mushrooms, are also high in Lentinan, a polysaccharide that has been used as a cancer prevention and treatment agent.
Health Benefits of Mushrooms
Mushrooms have been linked to a variety of health benefits due to their unique nutritional profile and antioxidant content. Some of the potential health benefits of mushrooms include:
Improved immune function: Mushrooms contain beta-glucans, a type of carbohydrate that can help boost the immune system.
Reduced cancer risk: Some studies have found that eating mushrooms may be associated with a lower risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast and prostate cancer.
Improved gut health: Mushrooms are a good source of dietary fiber, which can help to support the growth of healthy gut bacteria and improve digestion.
Improved heart health: Some mushroom compounds, such as ergothioneine, may have anti-inflammatory properties that can help lower the risk of heart disease.
Lowering blood sugar levels: Some mushrooms, such as Agaricus blazei Murill (ABM), have been found to have an effect on blood sugar levels and may be beneficial to diabetics.
Weight loss: Because mushrooms are low in calories, fat, and fiber, they can be a good addition to a weight loss diet.
It is important to note that the majority of these benefits are based on observational studies, and more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Are Mushrooms Safe for Everyone?
Mushrooms are generally considered safe for most people to consume. They are a nutritious food that can be consumed as part of a healthy diet. Some people, however, may be allergic to mushrooms.
A mushroom allergy can cause skin rashes, hives, itching, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face, mouth, or throat. If you experience any of these symptoms after consuming mushrooms, you should seek medical attention right away.
In addition, some mushrooms, particularly wild mushrooms, may contain toxins that, if consumed, can cause serious illness or death. As a result, it is critical to understand the types of mushrooms you are eating and where they came from. If you are unsure of the type of mushroom or where it came from, it is best to avoid it.
Furthermore, people with autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease, or those with compromised immune systems, should avoid eating raw mushrooms because they may contain bacteria that can cause infections.
Is Mushroom a Vegetable or Protein?
Mushrooms are classified as a vegetable in the dietary guidelines because they have a similar nutrient profile and culinary applications to vegetables. They contain important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants and can be used in a variety of dishes.
The USDA recommends that adults consume at least 2.5 cups of vegetables per day, and including a serving of mushrooms (1/2 cup cooked or 1 cup raw) can help increase nutrient density and contribute to meeting the daily recommended intake for essential vitamins and minerals.
Furthermore, because mushrooms are a good source of protein, they can be used as a meat substitute for vegetarians and vegans, diversifying the sources of protein in the diet. As a result, determining the potential health benefits of including mushrooms as a regular part of the diet and how it can contribute to a well-balanced diet is the goal of assessing the nutritional impact of adding a serving of mushrooms in USDA Food Patterns.
Are Mushrooms Healthier Raw or Cooked?
Mushrooms can be either raw or cooked, and each preparation has its own benefits.
Due to the fact that cooking can reduce the vitamin D content of mushrooms, eating them raw might give you a greater amount. In addition, some research suggests that consuming raw mushrooms may aid to preserve their antioxidant qualities, which helps protect cells from free radical damage.
Cooking mushrooms, on the other hand, can make them more digestible and increase the bioavailability of certain nutrients, such as beta-glucans, a type of carbohydrate that can stimulate the immune system. Additionally, cooking can improve the flavor and texture of mushrooms, making them more appetizing.
Notably, certain varieties of mushrooms, such as shiitake mushrooms, contain the polysaccharide Lentinan, which has been utilized in cancer prevention and treatment. This polysaccharide can be released by cooking shiitake mushrooms, which can be useful for cancer patients.
Therefore, both raw and cooked mushrooms can be included in a healthy diet, and it is recommended to take them in a variety of ways to maximize their nutritional value. However, it is always essential to ensure that mushrooms are cleaned and stored properly to prevent food-borne infections.
What is the Healthiest Way to Cook Mushrooms?
Depending on your personal preferences and the dish you’re preparing, there are several healthy ways to cook mushrooms. Among the most popular methods are:
Sautéing: Sautéing mushrooms in a small amount of oil or butter over high heat is a quick and easy method. Sautéing can help to retain the natural moisture and flavor of the mushrooms while also providing a crispy texture.
Grilling: Grilling adds a smoky flavor and a slightly crispy texture to mushrooms. They are an excellent choice for a BBQ or as a side dish.
Roasting: This method involves cooking mushrooms for a longer period of time in a hot oven. Roasting mushrooms can help to bring out their natural sweetness and concentrate their flavor.
Steaming: Steaming is a healthy cooking method that can help to preserve the nutrients and texture of mushrooms. Over a pot of boiling water, place a steamer basket or a colander.
Stir-frying: Like sautéing, this method involves cooking the mushrooms over high heat while constantly stirring them. It is a quick way to cook mushrooms and is ideal for incorporating them into a stir-fry dish.
Whatever method you use, avoid overcooking the mushrooms as this can cause them to become tough and lose their flavor. It is also a good idea to thoroughly clean the mushrooms before cooking to remove any dirt or debris.
How to Add Them to your Diet?
There are numerous ways to incorporate mushrooms into your diet. Here are a few recommendations:
Add them to your salad: To add flavor and nutrition to your salad, slice mushrooms and add them to it.
Use them as a pizza topping: Mushrooms can be a tasty pizza topping, adding texture and flavor to the dish.
Incorporate them into soups and stews: Mushrooms can add a nice depth of flavor to soups and stews, and they also make an excellent meat substitute for vegetarians and vegans.
Use them as a meat substitute: Mushrooms have a meaty texture and can be used as a meat substitute in a variety of dishes, including burgers, stir-fries, and tacos.
Make a mushroom omelet: For a flavorful and nutrient-dense breakfast, add sliced mushrooms to your omelet.
Add them to your sandwiches: Sautéed mushrooms add flavor and nutrition to sandwiches.
Serve as a side dish: Sauté them with herbs, garlic, and olive oil and serve as a side dish.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mushrooms are an adaptable and tasty ingredient that can be utilized in several ways. In addition to being rich in important nutrients, they have been linked to a range of health advantages. They are an excellent source of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. They can be eaten raw or cooked, and each preparation has its own merits. Mushrooms can be easily and deliciously incorporated into salads, pizzas, soups, stews, sandwiches, and omelets, among other things. They can also serve as an alternative to meat for vegetarians and vegans. Before making large dietary changes, it is usually advisable to consult a healthcare practitioner, as certain individuals may be allergic to mushrooms.