Ackee is a tasty fruit with yellow or red skin that doesn’t have any cholesterol or saturated fat. It contains nutrients that are good for the body, including potassium, magnesium, calcium, and salt as well as protein, carbohydrates, and vitamins. It is also useful in cooking and offers a variety of nutritional advantages.
Ackee is a vibrant and tasty fruit that is a favorite ingredient in many unusual meals and has established itself as a staple in Caribbean cuisine due to both its flavor and its health benefits. This fruit, which has the scientific name Blighia sapida, is actually native to numerous countries in West Africa, not Jamaica, but it was probably carried there aboard a slave ship in the 18th century when it gained notoriety worldwide.
What is Ackee Fruit?
The ackee fruit, which is regarded as Jamaica’s national fruit and grows on evergreen trees, is readily available all year long. It is known as achee, akee, and ackee apple and grows on a West African native tropical evergreen tree.
When the pods are bright red and they readily break apart to reveal the delicious fruit inside, the fruit is completely matured, ripe, and ready for cooking. Jamaicans frequently claim that the fruit will “yawn” or “smile” before it is ready to be plucked from the tree, meaning that it will naturally open on its own. Large, glossy black seeds are hidden beneath three or four cream-colored arils when the pod is opened. You consume the arils.
Before eating, ackee needs a little bit of preparation, but it’s not laborious. Simply remove the crimson lining on each piece of meat and the black seeds from the flesh. You want the actual flesh, so throw away the rest. Before using the flesh in cooking, give it a thorough rinsing with tap water.
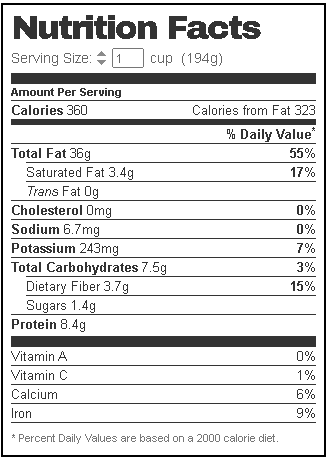
Ackee Fruit Nutrition Facts
Health Benefits of Ackee fruits
Produces Energy
Vitamin B3 sometimes referred to as the primary vitamin, is found in ackee fruit. It is a necessary ingredient for the body’s efficient conversion of food into glucose as well as the production of energy and macromolecules. The vitamin also improves blood circulation throughout the body and lowers blood cholesterol levels.
Prevents Scurvy
The fruit has a high concentration of vitamin C, an antioxidant that strengthens the immune system and shields the body from certain shortages like scurvy.
The vitamin C concentration of ackee fruit is important since it aids in the prevention of bruising, bleeding gums, and other dental-related illnesses.
Promotes Red Blood Cell Production
Iron is abundant in it, which is essential for both the production of red blood cells and effective oxygen distribution throughout the body. The fruit’s iron concentration also aids in preventing anemia, which happens when the body lacks enough iron.
Folic acid, which aids in the synthesis of red blood cells and is crucial in many anemia treatments, is also included in it.
Ackee fruits also contain vitamin C, which aids in the body’s absorption of iron-containing minerals. As a result, they all collaborate to help the body’s red blood cells improve.
Protects the Heart
Since ackee fruit contains no cholesterol, it is well known that it protects the heart by lowering blood cholesterol levels. It includes good fats like linoleic and stearic acid.
The ingredient makes it heart-healthy since the unsaturated fats, as previously indicated, reduce the risk of a number of heart ailments and diseases by controlling the body’s cholesterol levels.
One of the key roles of this kind of fat is to eliminate some of the so-called “unhealthy” saturated fats from the body, reducing the risk of heart issues, strokes, and even atherosclerosis.
Helps in Digestion
The fruit’s modest fiber level aids in normal digestion and bowel movement regulation, reducing the risk of constipation.
The fruit’s high fiber content aids in the production of bulk stools and guards against any digestive issues including bloating, cramping, and other illnesses that could cause colon inflammation.
Good for Weight loss
Due to its nutritional benefits, it can be utilized in weight loss programs and as a vegetarian source of protein. Although its protein concentration is modest compared to other foods that include protein, it is sufficient for fruits because most fruits contain little or no protein.
As a result, it aids in the development of the body’s tissues, cells, and so on. Due to its high fibre content, it is also ideal for weight loss because it acts as a roughage that aids in digestion but is not digested by the body. The fibre content aids with weight loss by making one feel fuller and reducing cravings.
Regulates Blood Sugar Level
People with type 2 diabetes can benefit from ackee, which is typically used to control blood sugar levels.
Ackee fruits contain nutritious complex carbohydrates that are richer in nutrients than simple carbohydrates, though both are processed by the body into glucose, which gives the body energy.
It contains more fiber since it is a complex carbohydrate and is more difficult to digest than other foods. As it aids in lowering blood sugar levels, which could have contributed to a blood sugar increase, ackee becomes a fruit for those people with simple sugars. It is also advised as a fantastic source of beneficial complex carbs, which aid in the control of insulin and blood sugar.
Lowers Blood Pressure
Ackee has a high potassium content, a mineral that lowers blood pressure. It is a healthy fruit that is suggested for those with hypertension because it will lower blood pressure.
The potassium in the fruit serves as a vasodilator in the body, helping to relax the muscles and widen the blood vessels in order to prevent vasoconstriction.
This function aids in preventing muscle and artery contractions that could raise blood pressure and cause hypertension, atherosclerosis, and other cardiovascular diseases like heart attack and stroke.
For Healthy Bones
Ackee fruits are rich in essential minerals that are excellent for bones, including calcium, which is known to aid in the formation of bone structures, and potassium, which collaborates with calcium to provide bone strength.
Another mineral found in ackee fruit is zinc, which aids in the bones’ improved absorption of calcium. Iron strengthens bones, which aids in bone growth.
Together, these minerals support a healthy bone structure, aid in bone healing, and stop the bone from losing important minerals. Additionally, it can aid in the prevention of osteoporosis, a disorder that weakens and changes the structure of bones.
Prevents Muscle Cramps
The body requires potassium and sodium for proper electrolyte balance, which is necessary for the proper operation of all body cells and organs.
These two elements are found in ackee fruits; whereas sodium is known to cause muscle contractions, potassium has the reverse effect by relaxing muscles.
Therefore, these two minerals are crucial and may be obtained from fruits while we consume lots of water to keep us hydrated and prevent muscle cramps. Muscle cramps are caused by an imbalance of electrolytes in the body and dehydration.
Good for Pregnant Women
As it helps to supply them with natural folic acid, which is required for the efficient growth and development of the fetus, folic acid is one of the vital supplements advised for TTC moms and pregnant women.
Additionally, it serves a crucial function in preventing DNA alterations in the body that could cause cancer or other negative effects.
Where to Buy Ackee?
Jamaica produces a lot of ackees, and the nation exports and cans the fruit around the world. Since the FDA forbids the importation of fresh ackee and even much of the canned product unless it has been “green listed,” which means the FDA has inspected it and determined it to be safe, you are unlikely to find it fresh in the United States.
All of these precautions are necessary because unripe ackee, comprising both pods and seeds, can result in a condition known as Jamaican vomiting sickness due to the presence of hypoglycin. Because the artificial amino acid hypoglycin is not eliminated during the canning process, canned ackee is largely prohibited in the United States. Only unripe ackee is aware of this risk. The pods are usually ripe and there is no risk of sickness if they are bright red and easily break apart.
If you are able to get canned ackee, make sure to drain it well before using. It is frequently brine-packed even if it has already been cooked. Once it has been added to the food you are cooking, mix it gently only once to avoid breaking up the meat.
What does Ackee Taste Like?
There is simply no other way to put it: Ackee is a peculiar fruit. Despite having a similar appearance to lychees and tasting like it should be sweet, ackee has a far more vegetal flavor and mouthfeel that even approaches that of starch.
Ackee’s mild, savory flavor is sometimes compared to that of nuts like almonds or legumes like chickpeas, despite the fact that when chopped and cooked, ackee really looks and tastes like scrambled eggs with its pale yellow hue and creamy, delicate texture.
As was already established, the ackee fruit’s seeds are extremely poisonous, and eating the flesh before it is fully ripe can be risky. Because of this, ackee is only accessible in the canned, pre-made form in the United States. When handling the fresh fruit, you should take the seed out of each piece of flesh and throw away the pink outer skin. After that, you can prepare to cook the flesh by rinsing it. You might be surprised by the meals you can prepare.
Is Ackee Good for your Heart?
It contains significant amounts of calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, fiber, and vitamin A. Ackee consumption has been linked to improved immune function, weight loss, blood sugar control, bone health, improved heart health, and protection against macular degeneration.
The ackee fruit is also a good source of vitamin A, an antioxidant that may help prevent inflammation and free radical damage. In addition to supporting the immune system, vitamin A is helpful for the health of the skin, eyes, and cells.
Vitamin C, another antioxidant, is present in ackee. The high-fat content of ackee has been thought to raise cholesterol levels, however, studies have shown that these lipids are actually beneficial to health. These polyunsaturated fatty acids aid in the regulation of cholesterol.With grilled plantain and sautéed greens, ackee, and saltfish. Making simple, nutritious versions of the meals you love. Several nutrients, particularly fatty acids, which are known to lower the risk of coronary heart disease, are abundant in ackee.
Is Ackee Good for Diabetes?
Ackee includes a significant amount of dietary fiber, which is advantageous for maintaining digestive health. Fiber promotes healthy bowel movements, reducing numerous stomach-related problems like obesity and constipation. Additionally, it lowers the risk of type 2 diabetes and gastrointestinal disorders.
The capacity of ackee to control blood sugar levels is one of its most unexpected health advantages. Ackee aids the body’s improved utilization of insulin, resulting in the stabilization of blood sugar levels. Those who have diabetes or prediabetes would particularly benefit from this.
The water used to cook the unripe fruit may also be lethal. The unripe fruit has toxins in it that might damage the liver. Along with dangerously low blood sugar levels, convulsions, and even death, the unripe fruit can also cause. Ackee is a fruit-producing plant. South Florida, the Caribbean, Central America, and West Africa are all places where it can be found. Ackee fruit is consumed in Jamaica as food and is regarded as a staple meal. Unripe ackee fruit, however, is extremely poisonous.
Is Ackee Good for Weight Loss?
Ackee is quite effective at promoting weight loss. The fruit is rich in fiber and includes a number of minerals, such as potassium, magnesium, and folate, that aid in regulating digestion. If properly prepared, ackee is a healthy and safe dish to eat.
According to the National Institutes of Health, “Ackee is an unsaturated fat and provides extra health benefits due to its high protein level, being an excellent source of vitamins B and C, zinc, calcium, and fiber” (NIH) All three experiments found similar relative fatty acid compositions for the ackee oils.
Oleic acid (55.44%), palmitic acid (25.57%), and stearic acid (12.59%) were the three main types of fatty acids; linoleic acid was present in small to undetectable levels. The Culture, Health, Arts, Sports, and Education (CHASE) foundation financed a study to determine whether Jamaica’s national fruit, ackee, promotes prostate cancer in males. The study’s findings show that ackee is safe to eat.
Conclusion
Ackee is a fruit that looks like a pear and grows on an evergreen tree. It starts off as a green fruit that ripens into a yellow, orange, and finally scarlet fruit that is easily recognized. The aril, which is the edible portion of the fruit, is finally revealed when the fruit splits to show three sizable black seeds encircled by spongy flesh.
The most well-known component of Jamaica’s national cuisine, saltfish, and ackee is ackee, which is adored at practically every store and street on that Caribbean island. More significant than its taste and accessibility are the fruit’s abundance of vitamins, nutrients, and natural ingredients, which make it an effective dietary supplement for a variety of medical ailments.