The seeds of watermelons are among the most nutrient-rich seeds available. They are a rich source of, among other nutrients, proteins, vitamins, omega-3, and omega-6 fatty acids, magnesium, zinc, copper, and potassium. Did you know that eating watermelon seeds reduces the nutritional value of this fruit? Yes, the fruit’s black seeds are both tasty and nutritious, making them the perfect snack.
Simply dehydrate and roast some watermelon seeds, and you’ll have an appetizing snack. Include some of these with your nut assortment to provide your body with a nutritional boost.
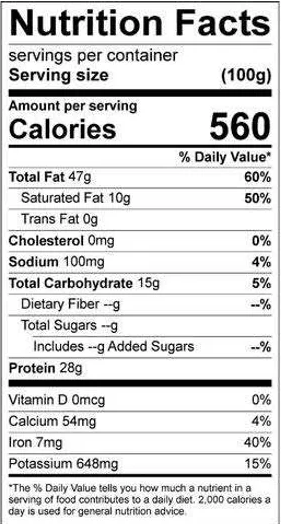
Watermelon Seeds Nutrition Facts
Health Benefits of Watermelon Seeds
You may be accustomed to spitting them out as you consume seeds; however, anyone can participate in a seed-spitting contest. Some people just opt for seedless. However, the nutritional value of watermelon seeds may change your mind. The seeds of watermelon are low in calories and rich in nutrients. When roasted, they become crisp and can easily replace unhealthy snack alternatives.
Optimizes Skin Health
As they are rich in vitamin C, antioxidants, etc., sprouted watermelon seeds help to purify your skin. Its oil is widely utilized in numerous anti-acne and anti-aging beauty products. The magnesium found in watermelon seeds helps to improve the overall appearance of the skin.
It is used to treat dry, itchy skin conditions such as eczema and other skin conditions. The seeds of watermelon act as a moisturizer for dull, dry skin. Due to its ability for protein synthesis, cell division, and repair, the zinc found in the seeds can slow down the aging process.
Aids in Hair Strengthening
Everyone appreciates healthy hair. Consequently, why not use watermelon seeds? The proteins, iron, magnesium, zinc, and copper found in watermelon seeds are known to improve hair quality. These seeds aid in hair growth and strengthening. The manganese present in the seeds prevents hair loss and damage.
Enhances Cardiac Health
In numerous ways, watermelon seeds can promote heart health. Having a high concentration of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. According to studies, these healthy fats protect against heart attacks and strokes. This seed is rich in magnesium, which maintains heart health and maintains normal blood pressure.
It is likely that the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and vasodilator (widening of blood vessels) properties of watermelon seeds contribute to their benefits for a healthy heart. Iron is essential for transporting oxygenated blood throughout the body. Zinc, which is abundant in watermelon seeds, plays a crucial role in heart health. It controls calcium movement in the heart.
Reduces Blood Glucose Levels
If you suffer from fluctuating blood sugar levels, try incorporating these magical seeds into your diet. Magnesium regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, which affects blood sugar levels directly. These seeds aid in the treatment of diabetes type 2.
Enhance the Immune System
Iron and minerals abundant in watermelon seeds improve immune function. These seeds also contain vitamin B complex, which contributes to this effect.
Prevent Osteoporosis
Include watermelon seeds in your diet if you have weak bones or conditions such as osteoporosis. As they are rich in magnesium, copper, and potassium, eating watermelon seeds regularly can prevent bone disorders.
Facilitates Nervous System
Watermelon seeds are an excellent source of vitamin B, which helps maintain a healthy brain and nervous system. Additionally, it is useful for mood disorders and dementia.
Boosts Energy Levels
Rich in micronutrients, watermelon helps to increase and sustain energy for an extended period. Despite the fact that many people are unaware of them, these magical watermelon seeds are incredibly tasty and nutritious. You can consume them as a snack whenever you feel hungry, and they will sustain your energy for a longer period of time.
Boosts Metabolism
Folate, iron, zinc, copper, magnesium, potassium, amino acids, and Vitamin B complex are commonly found in abundance in watermelon seeds. These nutrients are extremely beneficial for regulating and enhancing the body’s natural metabolism.
Reduces the Side Effects of Asthma
As a result of their high Vitamin C content, watermelon seeds are useful for the management of asthma symptoms. Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that can help alleviate the symptoms of asthma. Existing studies on the effects of watermelon seeds on asthma are suggestive, but additional research is required. However, watermelon seeds are safe to consume and should be a consideration for individuals with asthma.
Reduces the Risk of Developing Prostate Cancer
Lycopene is an organic chemical compound that is present in both watermelon and its seeds. According to research, lycopene possesses potent anticancer properties. Lycopene can be used to prevent the onset and/or progression of prostate cancer, according to a study published in 2015.
Reference: Phytochemical and Antibacterial properties of the seed of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus)
Is it OK to Eat Raw Watermelon Seeds?
The short answer is yes, and there’s no need to worry about your stomach turning into a watermelon. Raw watermelon seeds can be consumed directly from the fruit. They are non-toxic, and the seeds cannot germinate in stomach acid. You are not prohibited from consuming watermelon seeds. In fact, you can utilize them in a variety of ways to reap their nutritional and flavorful benefits. For instance, you can roast the seeds of a watermelon.
Roasted watermelon seeds are rich in nutrients and contain omega-3 and other healthy fatty acids. Not much happens when you eat raw watermelon seeds. In essence, they simply pass through your digestive system undigested, much like when you swallow a piece of gum. About 0.29 milligrams, or 1.6 percent of the recommended daily intake, of iron, can be found in a handful of watermelon seeds. Although it may not seem like much, the NIH only advises individuals to consume 18 mg each day.
Which is Better Watermelon Seeds or Pumpkin Seeds?
Compared to pumpkin and sunflower seeds, dried watermelon seeds are richer in protein and minerals. Comparatively, 11.9 grams of protein, 34.4 grams of carbohydrates, and 42% of the daily required magnesium intake may be found in 1 cup of pumpkin seeds. The protein content in the same amount of sunflower seeds is only 9.6 grams. One of these two is what most clients are accustomed to. Melon kernels don’t look the same since their two colors, light green and dark green, are distinct. Melon kernels look completely different from pumpkin kernels and are a creamy white tint.
They also almost exactly match the composition of pumpkin seeds. If you’d prefer, you can also consume the seed intact (which is what we do). They have a flavor that is identical to roasted pumpkin seeds, however, some people might not enjoy the thick, crunchy seed coating. According to studies, the antioxidants in pumpkin seeds also raise your body’s nitric oxide levels. This chemical acts to maintain the health, flexibility, and smoothness of your blood vessels, enhancing blood flow and lowering your risk of heart and circulation issues.
How do you Eat Watermelon Seeds for Weight Loss?
The nutritious watermelon seeds should be consumed along with the red, luscious flesh. Watermelon seeds have high nutritional content and few calories. Try roasting them and eating them as a snack if you don’t like to chew them with the fruit. Your impulsive urges will be replaced by a nutritious alternative.
Even though these super seeds are excellent for your health, eating too much of them can make you gain weight. To satisfy hunger at midday or at night, roasting them is the best way to consume them. According to experts, you should have no anxieties.
It’s completely fine to eat watermelon seeds. It’s quite fine if some seeds end up on your tongue along with the luscious, delicious watermelon flesh. Naturally, they won’t taste well, so if you’re looking for something a little more intriguing, keep reading. Lycopene, a vitamin found in watermelons, is wonderful for your vision and also supports heart health. They are also very healthy to eat in the heat since they are heavy in the water, which keeps us hydrated. It aids in weight loss in addition to assisting in surviving the heat.
Can I Eat Black Watermelon Seeds?
A typical watermelon’s black seeds are just regular seeds. If you sowed a couple of these mature, viable seeds in the earth, they would grow into watermelon plants. They are entirely safe to eat despite the misconception that they are too hard to eat.
Although both are healthy foods, most people spit out the black seeds because they are difficult to chew and make eating the watermelon flesh more difficult, according to Shames. However, it’s okay if you’re too preoccupied with eating the watermelon slices to bother with picking out the seeds. If you do swallow one, you’ll be fine.
But did you realize that these dark seeds have special nutritional qualities? The small seeds are extremely wholesome and nutritious. Because it is filled with nutrients and vitamins and contains 92% water, watermelon is a fantastic fruit for hydrating the body. Its seeds are incredibly nutrient-dense.
Clinical studies have shown that black seed can ease asthma symptoms by lowering inflammation and relaxing smooth muscles. These results support the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases and the relief of associated symptoms when combined with its antioxidant qualities.
Why are Watermelons with Seeds More Expensive?
Watermelons without seeds are invariably hybrids. This makes seeds more expensive. These sterile, seedless plants can produce fruit if pollinated by regular pollen from a watermelon with seeds or another compatible pollinator, despite the fact that they are sterile.
Watermelons without seeds are preferred over watermelons with seeds because they are easier to use and can have a better flavor. If you wish to chew and eat the seeds, seeded watermelons are less expensive and provide a lot of nutrients. Watermelon seeds have nutritional benefits, as I already explained.
Consuming watermelon in moderation is safe for diabetics. But it’s ideal to eat watermelon and other high-GI fruits with foods that are rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats. which, according to the National Watermelon Promotion Board, can be classified as either a fruit or a vegetable, and is very nutritious. According to nutritionists, watermelon is an excellent complement to a balanced diet because it is low in calories and sugar and packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Conclusion
As watermelon seeds are abundant in nutrients such as proteins, essential fatty acids, magnesium, and zinc, they provide unexpected benefits to our bodies. Here are several of the most significant benefits: Due to its high water, mineral, and vitamin content, watermelon is a fruit with exceptional hydrating properties. Its seeds are exceptionally nutritious. Low in calories and rich in micronutrients, such as zinc, magnesium, and potassium, these seeds also contain few calories. Watermelon seeds are prominently featured on the Diabetes Food Chart due to their positive effects on immunity, heart health, and blood sugar regulation.