Blueberries are a popular and sweet fruit that originated in North America and is now commercially farmed throughout the Americas and Europe. They’re low in calories and high in nutrients, with the potential to help with blood sugar regulation and heart and brain health. Blueberries are a good source of numerous vitamins, beneficial plant compounds, and antioxidants and are often touted as a super food. To know blueberry nutrition facts, read further.
Blueberry Nutrition Facts
Blueberries Have a Lot of Health Benefits
Anthocyanin, a type of flavonoid, is responsible for many of blueberries’ health advantages. Flavonoids are plant chemicals with potent antioxidant properties. The blueberry’s unique blue color is due to anthocyanin, and it also contributes to blueberries’ various benefits. Consuming a wide array of fruits and vegetables has long been linked to a lower risk of various lifestyle-related illnesses.
Obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and general mortality have increased the consumption of plant foods like blueberries. Plant foods may also help with hair and skin health, vitality, and overall weight loss.
Bone Health Maintenance
All blueberries are iron, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, and vitamin K. Each is a bone component. A balanced diet rich in these minerals and vitamins aids in the development and maintenance of bone structure and strength. Iron and zinc play critical roles in preserving bone and joint strength and flexibility, and vitamin K deficiency has been related to an increased risk of bone fracture. On the other hand, Vitamin K supplementation enhances calcium absorption and may minimize calcium loss.
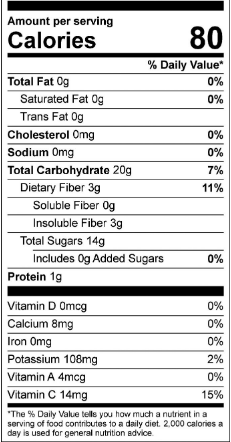
Certainly! Here are the nutrition facts for one cup (148 grams) of raw blueberries:
| Nutrient | Amount | % Daily Value* |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 84 | 4% |
| Total Fat | 0.5 g | 1% |
| Sodium | 1 mg | 0% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 21 g | 7% |
| Dietary Fiber | 4 g | 14% |
| Total Sugars | 15 g | N/A |
| Protein | 1 g | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 9 mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.4 mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 114 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 24 mg | 27% |
| Vitamin A | 80 IU | 2% |
| Folate | 9 mcg | 2% |
*Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your individual needs.
Collagen is the skin’s support system. It acts to prevent skin damage caused by the sun, pollution, and smoke by relying on vitamin C as a vital ingredient. Collagen’s capacity to smooth wrinkles and improve overall skin smoothness may also be improved by vitamin C. One cup of blueberries contains 24% of the daily required vitamin C requirement.
Blood Pressure Reduction
Maintaining low salt levels is critical for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Blueberries are sodium-free, and potassium, calcium, and magnesium are all present. Some studies have linked diets lacking in these minerals to elevated blood pressure, and it’s claimed that getting enough of these minerals in your diet will help you lower your blood pressure. Other research, however, has contradicted these findings. For example, in a 2015 research on adults with metabolic syndrome, daily blueberry eating for six weeks did not affect blood pressure.
Diabetes management
According to studies, people with type 1 diabetes who eat high-fiber diets had lower blood glucose levels, and people with type 2 diabetes who eat the same diet may have improved blood sugar, lipid, and insulin levels. The fiber content of one cup of blueberries is 3.6 grams (g). According to an extensive study published in the BMJ in 2013, some fruits may lower the incidence of type 2 diabetes in people. 6.5 percent of the patients got diabetes throughout the trial. Researchers discovered that eating three servings of blueberries, grapes, raisins, apples, or pears per week lowered the risk of type 2 diabetes by 7%.
Reducing the Risk of Heart Disease
It can assist in keeping your heart healthy. Blueberries are high in fiber, potassium, folate, vitamin C, vitamin B6, and phytonutrients, beneficial to heart health. Blueberries are also good for the heart because they don’t contain cholesterol. The fiber content aids in lowering total cholesterol levels in the blood and lowering the risk of heart disease. Homocysteine is a compound that vitamin B6 and folate prevent, and Homocysteine build-up in the body can damage blood vessels and cause heart issues.
According to a study conducted by the Harvard School of Public Health and the University of East Anglia, regular consumption of anthocyanin’s can reduce the risk of heart attack by 32% in the United Kingdom (UK). For young and middle-aged women, there is a reliable source. According to the study, women who ate at least three servings of blueberries or strawberries each week had the highest results.
Cancer Prevention
Blueberries include potent antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin A, and other phytonutrients that may help protect cells from disease-linked free radical damage. According to research, antioxidants may inhibit tumor growth, reduce inflammation in the body, and help prevent or slow the progression of esophageal, lung, mouth, pharynx, endometrial, pancreatic, prostate, and colon cancers. Blueberries also contain folate, which aids in creating and repairing DNA, and this can help to prevent cancer cells from forming. Because of mutations in the DNA, this source can be trusted.
Improving Mental Health
Blueberry eating has been linked to a reduced rate of cognitive deterioration in population-based research. In older women, this is a reliable source. Blueberries improve short-term memory, motor coordination, and cognitive impairment.
Healthy digestion, Weight Loss, and Feeling full
Because of their high fiber content, blueberries assist in avoiding constipation and maintaining regularity for a healthy digestive tract. Dietary fiber, which acts as a “bulking agent” in the digestive system, is well acknowledged as having a significant role in weight loss and management. Satiety, or the sense of being full, is increased by high fiber diets, and appetite is reduced. A person’s overall calorie intake might be reduced by feeling fuller for longer.
How Many Blueberries Should you eat a Day?
The consumption of 150 grams of blueberries each day can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by 15%. According to the researchers, blueberries and other berries should be included in dietary recommendations to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, especially among at-risk groups. According to a new study, eating a cup of blueberries every day lowers risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Consuming 150 grams of blueberries each day lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease by up to 15%. A 0.5 cup daily dose of blueberries is appropriate for a healthy adult in nutrition. Check with your doctor before adding them to your diet if you have an underlying health condition like Salicylate sensitivity.
Is the Sugar Content of Blueberries High?
Blueberries have a moderate quantity of sugar (15 grams per cup) (148 grams). They do, however, have no negative impact on blood sugar levels, which could be related to their high bioactive chemical concentration. Blueberries may induce a rash, headaches, or various gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals who can’t take salicylates, such as nausea, vomiting, reflux, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation.
The salicylate content of blueberry juice is exceptionally high. Blueberries, like most fruits, are frequently advised for constipation alleviation. They soften your stool and increase bowel movement frequency since they are high in water and fiber.
Blueberries or Strawberries: Which is Better?
Summary. Strawberry is higher in minerals, has five times the amount of Vitamin C, three times the amount of Folate, and has a lower GI, sugar content, and saturated fat content than blueberry. More vitamins, copper and zinc, carbohydrates, and monounsaturated fats are found in blueberries. It’s also less expensive than strawberries. Strawberries, cranberries, and blueberries are powerful blood thinners, among other fruits in the berry family.
In the same way, oranges, tangerines, cherries, raisins, prunes, pineapples, and tomatoes operate. Antioxidants are abundant in berries, including blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries. Antioxidants induce oxidation and protect you from sleep disturbance stress, according to National Sleep Foundation researchers.
Is it True that Blueberries Prevent Colon Cancer?
Strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, for example, are high in fiber, water, and antioxidants, which function as natural digestive cleansers and maintain your colon healthy. According to an animal study presented Sunday in Chicago at the 233rd national meeting of the American Chemical Society, pterostilbene, a natural antioxidant found in blueberries, may help prevent colon cancer.
According to new research, blueberry fiber is vital for reducing and protecting against bowel inflammations such as ulcerative colitis. When blueberries are combined with probiotics, the preventive impact is enhanced. Blueberries are well-known for their antioxidant and nutrient content.
Is it Healthy to Eat Frozen Blueberries?
Because frozen blueberries are high in fiber, they can help keep your digestive system regular, reducing constipation and supporting a healthy digestive tract. However, research suggests that frozen blueberries may have a health advantage over fresh berries. South Dakota State University research found that freezing blueberries increases their antioxidants.
After berries have been collected, food handlers, pieces of machinery, and equipment might contaminate them. During freezing, mixing, or packaging, the bugs might spread, and the berries may become dangerous to eat due to this.
Conclusion
Blueberries are widespread perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. In Vaccinium, they are Cyanococcus. Cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries, and Madeira blueberries are all members of the Vaccinium genus. All commercial blueberries are native to North America, both wild (low bush) and cultivated (high bush). Europe introduced high bush varieties.