Green bananas are the same bananas you’d eat for breakfast or a snack if they were ripe, but in the Caribbean, they’re used as vegetables, mostly in savory meals. Green bananas may have additional nutrients and benefits not found in yellow bananas. They’re high in resistant starch and pectin, which are filling, beneficial to digestion, and aid with blood sugar control. On the other hand, some dislike green bananas because of their bitter taste and mushy texture. To know green banana nutrition facts, read further.
Green bananas, also known as unripe bananas, have not yet converted all of their resistant starch into digestible sugars in the body. Although they are not as sweet or tempting as ripe bananas, there is no harm in incorporating this fruit into your diet. The starch in bananas is turned into sugar when they ripen, making them sweeter. All of this may not seem significant—after all, green and yellow bananas are high in potassium, vitamin B6, fiber, and vitamin C and contain significantly less sugar than a doughnut.
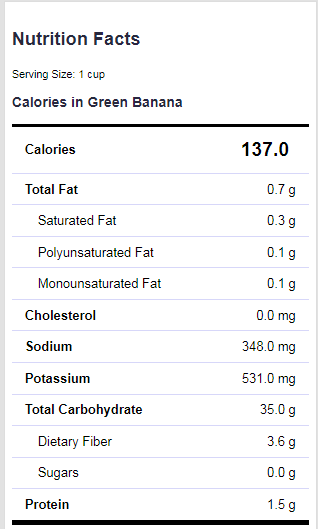
Green Banana Nutrition Facts
Health Benefits of Green Bananas
1. May Improve Digestive Health
Green bananas have traditionally been used to treat constipation, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and other gastrointestinal problems. Green bananas are a good source of fiber, and the vitamin aids in stool thickening and improved bowel movements. This helps to promote digestion and prevent constipation, and it also aids in the prevention of colon cancer.
Complex carbs make up resistant starch, broken down in the gut. For the gut microbiome, this fiber functions as a prebiotic. This fiber is used by gut bacteria, which converts it into vital nutrients that the body can utilize. Short-chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, are examples of such byproducts.
Green bananas may help with constipation as well as diarrhea. According to a mouse study, they may be helpful for youngsters with recurrent diarrhea. Green bananas may be effective against mucosal ulcers in the stomach.
2. May Help Lower Blood Sugar
Green bananas, like all fruits, have a low glycemic index (around 30). As a result, consuming them can help you manage your blood sugar levels.
Low-glycemic-index foods slowly release sugars into the bloodstream. Sudden sugar surges may increase the risk of diabetes and other metabolic problems, such as cardiovascular disease. Unripe green bananas should be preferred to overripe yellow bananas by people with diabetes. Green bananas include pectin and resistant starch, which help keep blood sugar levels. This improves insulin metabolism, which is very beneficial for people with diabetes. Green bananas and their derivatives (such as green banana flour or starch) improved insulin sensitivity in rats.
3. May Aid Weight Loss
Green bananas are high in fiber and have a high resistant starch content. As a result, they’re a healthy, whole snack that keeps hunger at bay.
The high pectin content of green bananas fills your stomach, and eating fiber-rich foods boosts satiety levels. This reduces the likelihood of overeating. Excess calories are not consumed, which would typically lead to weight growth. The fiber in the diet has been related to a lower risk of obesity. Resistant starch promotes satiety and has been associated with weight loss. In obese people, pectin has slowed stomach emptying and increased satiety.
Green banana flour has been demonstrated to help with glucose balance and lessen hunger. Lower levels of ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and regulated insulin levels have also been associated with grain consumption. Consumption of green banana flour improved women’s lipid profile and body composition with higher-than-average weight research. Inflammation may be reduced by using flour.
4. May Help Promote Cardiovascular Health
Metabolic problems include cardiovascular illnesses. Obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease are all linked. Resistant starch is abundant in raw bananas. According to animal research, resistant starch helps keep cholesterol in check, and low cholesterol levels have been related to a lower risk of heart disease.
Green bananas have also been linked to a reduction in blood sugar, and they are helpful to people with diabetes. Potassium is abundant in green bananas, and the mineral has a vasoligating effect and it aids in the control of blood pressure in the body. Green bananas are a healthy choice for certain people, and not everyone, however, would be able to incorporate them into their diet.
What to Do With a Green Banana?
Green bananas are used in salads in the same way that potatoes are. You can also use them to make pies, like shepherd’s pie. There’s even a tasty pickled banana dish popular on the islands. Because of their high starch content, any fresh or dried bananas can readily be turned into porridge. Green bananas can be used to make chips or to stones when they’re fresh and thinly sliced, or they can be boiled and served with sautéed salt pork. They also serve delectable sweets.
Boiling green bananas, a typical preparation technique, is probably the easiest way to test your taste for them. Submerge the bananas in enough salted boiling water to cover them, peeling intact. Boil them for about 20 minutes or until the skin is readily pierced with a fork. That’s all there is to it. Slice the skin open and serve the bananas with a fish or pig main meal, like Jamaica.
Use the greenest bananas you can find, which may entail collecting them as soon as they’re placed in a produce bin in a supermarket in the United States. Bananas must be shipped in their green, unripe state because they will mature and ripen as they travel to grocers’ shelves. If producers shipped ripe yellow bananas, they would spoil them before reaching their destinations.
How to Eat Green Bananas?
Bananas in their natural state are green and unripe. They’re a little more difficult to peel, but they’re a tasty snack. They can be added to smoothies and yogurts, and they can be frozen and then dipped in dark chocolate. Green banana flour can also be used to make pasta.
Green bananas are yellow banana that has not yet ripened. These are high in vitamins and minerals, which aid in treating various diseases. Green bananas’ health benefits are due to their nutritional profile, and they may help with digestion, blood sugar control, weight loss, and cardiovascular health. However, some people may experience adverse side effects. Gas and bloating may occur in sensitive people or those allergic to latex. As a result, use caution.
What Does Green Banana Taste Like?
By weight, green bananas can contain up to 80% starch, and many people dislike the flavor and feel of these carbohydrates. As those starches are converted to sugars, starch in a ripe banana decreases to less than 1%. Then, as they ripen, more brown dots appear until they’re entirely black.
As a result, they’re ideal for sweet fried plantains like those served in Cuban eateries. They have a banana bread flavor to them.
What are the Side Effects of Green Banana?
Green bananas are generally regarded as safe to eat. Individuals with sensitive stomachs or allergies, on the other hand, may experience some discomfort. Bloating and gas are two examples of such symptoms. People who are allergic to latex may experience adverse reactions to green bananas. This is most likely because they both produce allergy-inducing proteins, and latex fruit syndrome is the name for this ailment. In some circumstances, eating green bananas the appropriate way can lessen the likelihood of these adverse effects.
Green bananas, in particular, have been demonstrated to be beneficial in the treatment of diarrhea. Bananas are also high in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics, which aid digestion. Foods that aid digestion may be essential for people with digestive conditions like irritable bowel syndrome. Bloating, gas, cramps, softer stools, nausea, and vomiting are all possible side effects of banana consumption. Bananas may induce high potassium levels if consumed in large amounts, and bananas can cause allergic reactions in certain people.
Conclusion
Some foods that produce diarrhea do so because they are consumed in excessive quantities; for example, a bite of a banana may not cause diarrhea in some people with IBS, but eating a whole banana may. Green bananas can help keep your gut bacteria in good shape, and they can also boost the formation of short-chain fatty acids, which are beneficial to digestion.
It include pectin and resistant starch, which can help manage blood sugar levels, especially after meals. Green bananas are considered healthy, yet some people may experience digestive issues due to eating them, and people who are allergic to latex may also have problems consuming them. Because it is difficult for humans to digest, the resistant starch that makes up a green banana is a good source of dietary fiber. Green bananas have a high pectin content, which is one of the reasons they stay hard until they ripen.