To begin, what exactly is a coconut? Is it a fruit? Is it a nut? Coconut can be a fruit, a nut, or a seed, which adds to the confusion. If you pick up a coconut that has fallen from a coconut palm, you’ll see that the exocarp layer is hard and green. The mesocarp is the husk (brown and hairy) beneath that layer. The endocarp, the seed‘s outer layer, is found inside. When you crack open the seed, you’ll see a white layer of coconut “meat” and liquid.
The use of coconuts has evolved over the previous decade, even though coconuts themselves haven’t altered. It’s no longer limited to sweet pia Coladas and candy bars. We use coconut oil in our cooking and our coffee, add shredded Coconut to cereal, incorporate frozen coconut sheets in smoothies, hydrate with coconut water, and even apply the oil on our hair and skin.
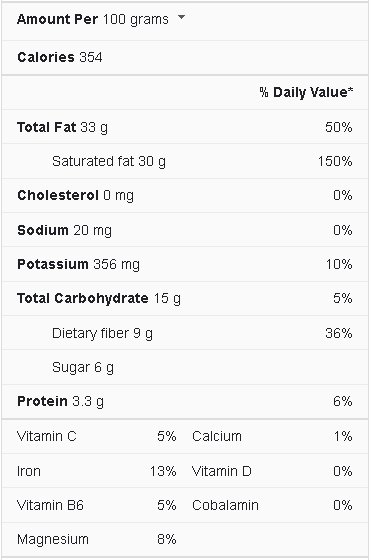
Coconut Nutrition Facts
How To Cook With Coconut At Home?
If you’re looking for ways to incorporate Coconut into your meals, consider the following:
- Replace 20 percent of the flour in a recipe with coconut flour if you’re baking with it.
- Coconut oil has a higher fat content than butter; thus, it’s better for baking. When substituting coconut oil for butter, you’ll need to use less of it.
- Coconut oil can be substituted for oil in any culinary recipe; however, make sure to select the type — virgin or refined — that best suits your preferences.
- Virgin coconut oil gives stir-fries and curries a lovely tropical coconut flavor when cooking. Coconut oil that has not been refined has a more neutral flavor.
- Instead of creamer, use coconut milk in your coffee.
- Coconut oil is used to make stovetop popcorn.
Health Benefits Of Coconut
Here are some health benefits of Coconut:
Highly Nutritious
Unlike many other fruits that are strong in carbohydrates, Coconut is primarily made up of fat. Protein, numerous essential minerals, and modest B vitamins are also present. They are, however, a minor source of most other vitamins. Coconut minerals are engaged in a variety of bodily functions. Manganese is particularly abundant in coconuts, and it is necessary for bone health and the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and cholesterol. Copper and iron, which aid in forming red blood cells, are also abundant, as is selenium, an important antioxidant that protects your cells. MCTs are metabolized differently than other fats in that they are absorbed directly from the small intestine and used for energy quickly.
May Benefit Heart Health
According to studies, people who live on Polynesian islands and eat coconut meat frequently have lower incidences of heart disease than those who eat a Western diet. However, because native Polynesians eat more fish and fewer manufactured goods, it’s unclear if the lower rates are related to coconut use or other dietary factors. Another study of 1,837 Filipino women discovered that those who consumed more coconut oil had higher HDL (good) cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, and triglycerides. According to the study, coconut oil negatively affected cholesterol levels. Virgin coconut oil, which is produced from dried coconut meat, has been shown to help people lose belly fat. This is especially advantageous because belly fat raises your risk of heart disease and diabetes.
May Promote Blood Sugar Control
Because Coconut is low in carbohydrates and high in fiber and fat, it may help keep your blood sugar in check. Coconut was discovered to have anti-diabetic properties in rat research, probably due to its arginine level. Arginine is an amino acid required to properly operate pancreatic cells secrete the hormone insulin to control blood sugar levels. When rats with diabetes were fed protein produced from coconut meat, their blood sugar, insulin levels, and other glucose metabolism markers improved dramatically compared to those who did not. In addition, beta cells with their pancreas began producing more insulin, a hormone that aids in blood sugar regulation. The high quantities of arginine in Coconut were also suspected of playing a factor in better beta-cell activity.
Contains Powerful Antioxidants
Phenolic chemicals found in coconut meat are antioxidants that may help protect cells from oxidative damage. The following are the most common phenolic compounds discovered:
- Gallic Acid
- Caffeic Acid
- Salicylic Acid
- P-Coumaric Acid
In lab experiments, coconut meat has been demonstrated to have antioxidant and free-radical-scavenging properties. It contains polyphenols that can prevent LDL (bad) cholesterol from being oxidized, making it less likely to form plaques in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. Antioxidants in coconut oil have also been proven in several test-tube and animal experiments to protect cells from oxidative stress and chemotherapy-induced cell death.
Easy To Add To Your Diet
Whether flaked or shaved, Coconut provides a beautiful flavor to savory foods. Curries, fish stews, rice dishes, and even breaded shrimp benefit from its meaty texture and flavor. Keep in mind that some brands have additional sugar, which you might not want in savory recipes. Always read the label to see what’s in the food. Shredded Coconut is a terrific addition to cookies, muffins, and quick loaves of bread because it gives a hint of natural sweetness and moisture. A sprinkling of raw Coconut on top of oats provides texture and a tropical flavor. It’s also a tasty calorie booster when mixed with pudding or yogurt for someone looking to gain weight. Coconut flour is used as a wheat flour alternative in baking. It’s gluten-free, nut-free, and a popular choice for carb-conscious people.
Potential Drawbacks
Coconuts are high in calories due to their high-fat content. If you don’t account for the extra calories elsewhere in your diet, they may cause weight gain depending on your calorie needs and intake. There is still a scarcity of high-quality research on Coconut, cholesterol, and cardiovascular disease. While eating Coconut in moderation is usually healthy, you should consult your doctor about it if you are at risk of developing heart disease. Additionally, though rare, some people are allergic to coconuts, and you should avoid any coconut-derived goods if you have this sensitivity.
Storage Tips
What sort of Coconut you buy will determine how you preserve it. Coconut’s high oil content causes it to turn rancid if not stored properly quickly. Depending on the freshness of the Coconut when purchased, it can be stored at room temperature for up to four months.
The fresh Coconut should be grated and placed in a firmly sealed container or plastic bag, and it can be kept for up to four days in the refrigerator or frozen for six months. Canned Coconut that hasn’t been opened can be kept at room temperature for up to 18 months, and Coconut in plastic bags can be kept at room temperature for six months.
Once opened, both of these should be chilled and used quickly: canned Coconut should be consumed within five to seven days, while dried Coconut should be consumed within four weeks.
Conclusion
Coconut has a tropical taste to it in all forms. The meat is a little nutty and crunchy, the juice is slightly milky, and the coconut milk is thick and creamy. The juice of a young coconut is less thick and creamy, tasting more like slightly sweetened water. Coconut may be used in various cuisines, from desserts to soups and main courses. It’s common in meals from tropical regions of the world, especially Thai cuisine, where Coconut is abundant. Coconut can also be used as a crust or marinade for fish. Smoothies, drinks like the pia colada, and other beverages often contain coconut milk and cream.