Cumin is a spice derived from the Cuminum cyminum plant’s seeds. Cumin is used in various recipes, particularly those from its native Mediterranean and Southwest Asian regions. Chili, tamales, and a variety of Indian curries all benefit from the flavor of cumin. It is earthy, nutty, spicy, and warm in flavor. Cumin has also been utilized in traditional medicine for a long time. Cumin’s traditional health benefits, such as improving digestion and decreasing food-borne illnesses, have been proven by modern investigations. New benefits, such as aiding weight loss and increasing blood sugar and cholesterol control, have also been discovered through research.
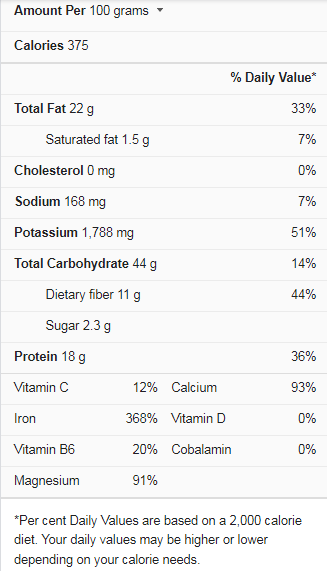
Cumin Nutrition Facts
Cumin’s Health Benefits
Cumin has been treating anything from indigestion to diarrhea to headaches for decades. It has been used to cure kidney and bladder stones, eye disorders, and even leprosy in India.
Antibacterial Effects
Studies have demonstrated cumin helps destroy bacteria that can enter your body and make you sick. Cumin has been demonstrated in the lab to inhibit the growth of microbes such as E. coli, which can cause food poisoning. Cumin’s antibacterial characteristics may explain its extended use as a preservative.
Cancer Prevention
Cancer arises when the body’s cells begin to grow uncontrollably, and these aberrant cells form tumors, which are clumps of them. In multiple animal experiments, cumin seeds have been found to inhibit the formation of several tumors, including those caused by liver, stomach, and colon malignancies. More research is needed to see if cumin can help humans avoid cancer.
Cholesterol Control
Cumin has been found in several trials to assist people in managing their cholesterol levels. Cumin powder dissolved in yogurt reduced “bad” (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides while boosting “good” (HDL) cholesterol, according to one study.
Diabetes Management
Cumin has been shown to help persons with diabetes manage their symptoms and consequences. Cumin, which has traditionally been used as an anti-diabetic medicine, has been discovered to help lower urea levels in the blood. According to one study, this organic substance may interfere with how your body responds to insulin. Cumin has also been proven in animal experiments to help maintain blood sugar levels in check, although further research is needed.
Improve Digestion
Cumin has been demonstrated in studies to aid with various digestive disorders. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms such as tummy pain, bloating, and the urgent need to go to the bathroom were significantly reduced by cumin extract in one study. Cumin has long been used as a traditional cure for diarrhea, and some preliminary research has found substantial evidence to back it up.
Weight Control
Cumin has been shown in several early studies to aid weight loss when consumed as part of a healthy diet. In one study, those who consumed cumin powder lost weight, had a smaller waist circumference, had less fat mass, and had a lower BMI (BMI). According to another study, cumin supplements may be as efficient as a weight loss medicine in lowering weight and BMI.
Irritable bowel syndrome
The benefits of ingesting cumin essential oil drops on the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome were investigated in a short pilot study conducted in 2013. (IBS). According to study participants, many symptoms improved after four weeks, such as stomach pain and bloating. Those with IBS who mainly had experienced constipation had more frequent bowel movements at the end of the research. Those who reported diarrhea as a primary symptom had fewer stool motions.
Stress
Cumin may assist the body in coping with stress. The effects of cumin extract on stress symptoms were investigated in rats. The animals’ bodies exhibited a considerably reduced stress response when given cumin extract before a stressful activity than when they were not given the extract. Cumin’s antioxidant properties may aid in combating the effects of stress, and cumin was a more potent antioxidant than vitamin C in the rats evaluated by the same researchers.
How Much Cumin can you Consume Daily?
Cumin is thought to be relatively safe and harmless, even in massive doses. However, if you want to utilize it, you need to be aware of potential adverse effects. Cumin is usually used in doses of 300 to 600 milligrams per day as a herbal supplement. Cumin seed is also known to contain narcotic qualities, so it should be used with caution. Cumin seeds also cause adverse effects to mental fogginess, tiredness, and nausea, and cumin seed eating in excess can cause nausea and sleepiness.
Cumin provides several health benefits that have been scientifically proven. Some have been known since antiquity, while others have only recently been found. Cumin as a spice boosts antioxidant consumption, aids digestion, offers iron, improves blood sugar regulation, and lowers the risk of food poisoning.
Cumin or Turmeric, Which is Better for Weight Loss?
Turmeric’s component, curcumin, has been shown to improve metabolism and help people lose weight. On the other hand, Cumin lowers fasting cholesterol, LDL, and Triglyceride levels in the blood and raises HDL levels. Turmeric’s role in weight loss has been studied recently. According to test-tube research, curcumin may reduce specific inflammatory indicators that play a role in obesity, and people who are overweight or obese have higher levels of these indicators.
Turmeric tea helps to enhance bile production in the stomach when consumed regularly. It’s a digestive juice that aids in fat emulsion and metabolism. As a result of this procedure, this spice is an excellent weight-loss aid. Turmeric milk, consumed before bedtime, may assist in improving your mood, and Turmeric may aid in relieving depression symptoms.
Is Cumin the Same as Coriander?
The coriander flavor is slightly sweet, and cumin has a more bitter flavor. Coriander has a lighter, brighter flavor than cumin, which is much warmer and more profound in flavor. Because these two spices are made from different plants, they have various nutritional properties and appearances. Cumin is a great stand-in for coriander because it’s frequently used and usually found in most spice racks. Cumin has a warm, nutty, spicy flavor similar to coriander’s earthy tones, albeit slightly distinct in taste.
Cumin can be used in place of coriander on a one-to-one basis. Although some people believe this, these two spices are not the same. Cumin and coriander are both members of the Apiaceae plant family. While they both contribute intensity or heat to a meal, they have different flavors. Coriander is a spice derived from the dried seed of Coriandrum sativum, an annual herb, and cumin is a spice made from the dried seed of Cuminum cyminum, a flowering plant.
Is Cumin Beneficial to the Kidneys?
A growing body of research suggests that black cumin and its vital component, thymoquinone (TQ), can protect kidneys from xenobiotics such as chemotherapeutic drugs, heavy metals, pesticides, and other environmental toxins. Black cumin can also help prevent ischemia shock in the kidneys. Cumin seeds contain a highly volatile oil that might cause liver and kidney damage over time, primarily induced by swallowing an excessive amount of seeds.
After 15 days, drink it twice a day. This beverage can aid people who are suffering from kidney stones. Even the coriander and cumin drink might help maintain your kidneys in good shape. Kidney damage can be reduced by eating a balanced diet low in sodium, processed meats, and other kidney-damaging items. Focus on fresh, naturally low-sodium items like cauliflower, blueberries, salmon, whole grains, etc.
Does Cumin Raise Blood Pressure?
Black cumin has been discovered to lower systolic blood pressure, suitable for blood pressure. It has been demonstrated to lower fasting glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels in glycaemic management. According to the researchers, this could be due to numerous essential chemicals, citing previous findings. Cumin can help lower blood pressure, and it’s anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant. It lowers blood pressure by increasing the availability of nitric oxide in circulation.
Nitric oxide widens blood arteries and reduces blood pressure. Cumin may make bleeding disorders worse by slowing blood coagulation. Cumin may help reduce blood sugar levels and slow blood coagulation during surgery, and it may impair blood sugar management and exacerbate bleeding during and after surgery. Cumin should be avoided for at least two weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Conclusion
Cumin has been a mainstay of the human diet for thousands of years. It’s grown worldwide, including the Middle East, the Mediterranean, India, and China. Today, most cumin sold in the United States comes from India. Cumin is a culinary spice, and the oil is used in perfumes worldwide. It’s also a well-known traditional medicine treatment that benefits a worthy purpose. Cumin has many health advantages packed into a small number of seeds.