It’s difficult not to like eggs because eating eggs has many health benefits. Eggs are nutrient-dense, which means they contain many vitamins and minerals for the number of calories. Eggs are high in protein and choline, and they also contain several B vitamins, as well as vitamins A and D. Whether you boil, scramble, fry, or bake your eggs, they are convenient and healthy (and, contrary to popular belief, will not raise your blood cholesterol levels).
Egg Nutrition Facts
How Healthy Is Eating Eggs?
“Including eggs at breakfast helps make it the most nutrient-dense of Americans’ dining times,” Kanter said, citing a 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee report. “Eggs can also be a nutritious addition to other meals and snacks, which are often deficient in vitamins and minerals…” Because eggs are low in calories and saturated fat, they can be a great complement to other nutrient-dense meals, particularly those that are often missing from Americans’ diets, such fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.” here are some health benefits of eating eggs:
Protein
Whole eggs are a complete protein containing all of the essential amino acids. Egg protein is so excellent for you that the World Health Organization uses it as a benchmark for assessing protein in other foods. “Eggs are completely natural and give one of the finest quality proteins of any food,” Kanter explained. “A single egg contains more than six grams of protein, or 13 percent of the necessary Daily Value (DV), with the yolk accounting for approximately half of the total.” Protein is beneficial for various reasons, including weight loss and heart health. “Although we often think of protein’s role in muscle growth and maintenance, emerging evidence reveals that protein has additional benefits,” Kanter added.
Eyesight
“The antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin, which are found in egg yolks, may help prevent macular degeneration, which is a primary cause of age-related blindness,” Kanter explained. “The two nutrients (like beta-carotene in carrots) belong to the carotenoid family.” The American Optometric Association notes the existence of these antioxidants in eggs. Eleven men and women supplemented their diets with 1.3 egg yolks each day for 4.5 weeks in a research published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. The participants’ levels of lutein and zeaxanthin increased by 28-50 percent and 114-142 percent, respectively.
Choline
“In the diets of Americans, eggs are one of the richest sources of choline,” Kanter added. One large egg can deliver 35% of your daily choline requirements, which is excellent news because, according to research published in The Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 90% of Americans are deficient in this nutrient.”Choline is a vital nutrient for pregnant and lactating women because it helps with brain and memory development,” Kanter added. The impact of choline on memory in babies was highlighted in an animal study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. “Their brain function changed, resulting in lifetime memory enhancement,” when rat pups were given choline supplements in utero or the first two weeks of life.
Weight Loss
Eggs are a low-calorie food that can be a good choice for dieters. “Eating eggs for breakfast may support a healthy body weight and lower the risk of obesity,” Kanter stated, citing their satiating characteristics (the capacity to make you feel fuller for longer). According to research published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition, women who ate egg-based breakfasts instead of bagel-based breakfasts ate less at lunch, during the day, and for the next 36 hours. According to a study published in the International Journal of Obesity, Dieters benefit from egg-based breakfasts. A group of overweight men and women were divided into four groups: those who ate egg breakfasts and were put on calorie-restricted diets, those who ate egg breakfasts but were not on a diet, those who ate egg breakfasts but were not on a diet, and those who ate bagel breakfasts and were put on calorie-restricted diets.
Is It Healthy To Eat Eggs Every Day?
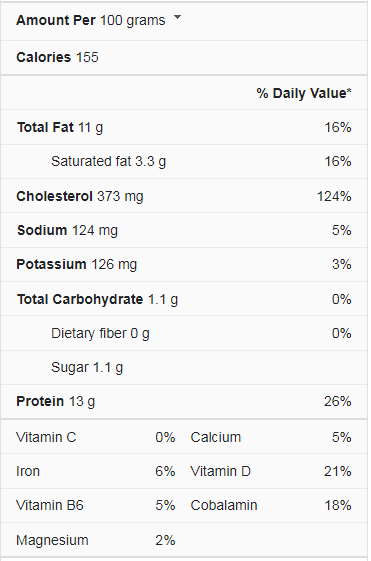
According to the nutritional breakdown, one egg has 75 calories, 5 grams of fat, 6 grams of protein, 0 carbs, 67 milligrams of potassium, 70 milligrams of sodium, and 210 milligrams of cholesterol. Eggs are also high in vitamins A, D, and B12 and choline, a necessary substance for numerous metabolic processes. Aside from the cholesterol, one egg is a nutritious breakfast, lunch, or dinner option. In comparison to other sources of cholesterol, research suggests that the cholesterol in eggs does not appear to harm the human body. Eggs, for example, are frequently consumed with other high-salt, saturated-fat, and cholesterol meals like bacon, cheese, and butter. These foods have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and should be consumed in moderation. Most healthy people can consume up to seven eggs per week without harming their hearts. Some people prefer to consume just egg whites and skip the yolk, which delivers protein without the cholesterol.
Risks of Eating Eggs
As previously stated, people with diabetes, high cholesterol, or hypertension should limit their egg intake. According to a study published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, people with diabetes who ate one egg per day were more likely to develop cardiovascular disease. For people with diabetes, eating egg whites instead of entire eggs may be a suitable option. According to the Harvard School of Public Health, everyone should pay attention to the trimmings that come with eggs. Cheese, ham, bacon, white bread, and other favorites can add a significant amount of calories and saturated fats to your diet.
Raw egg whites interfere with biotin absorption, according to research published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition in 2002. According to World’s Healthiest Foods, biotin is a B vitamin crucial for fat and sugar metabolism and blood sugar management. Avidin, a glycoprotein found in egg whites, binds to biotin and allows it to be absorbed by the digestive system. Cooking egg whites solves this problem. Whole eggs are a good source of biotin, providing around 27% of the daily required amount.
Conclusion
Vitamin A, vitamin E, and selenium, all of which operate as vital antioxidants in supporting eye health retina function, and helping to prevent degenerative vision as you age, are all found in eggs. Hard-boiled eggs are a great source of lean protein, and they’ll keep you satiated without consuming too many calories, which is beneficial if you’re trying to reduce weight. In addition to vitamin D, the protein in hard-boiled eggs helps to enhance fetal development.