There are a few telltale indicators that your bell pepper is terrible, and you may save money by eating the final one instead of tossing it out. A dash of pepper should be used within three to four days of purchase and free of brown or black blemishes. The pepper is terrible if the skin develops wrinkles. Weighing a pepper is the best way to tell if it’s rotten. Some bells have a thinner middle, while others have a thicker middle. The pepper’s weight is a good indicator. A bell’s skin usually is smooth and wrinkle-free.
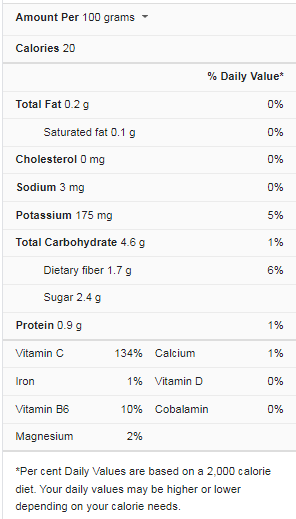
Green Bell Pepper Nutrition facts
How to Tell If Green Bell Peppers Are Bad?
Here are few signs of a bad green bell pepper:
- Have huge sunken patches or are soft to the touch. This means they’ve lost moisture and are no longer edible in most circumstances.
- They are beginning to decay or mold. You can take out little pieces of ruined or broken vegetables, as you probably do with most vegetables.
- In any manner, smell bad.
- Bell peppers are vibrant and flavorful, and they brighten up whatever dish they’re added to. They don’t keep fresh for long after you harvest them off the pepper plant, so determining whether the vegetable you want to freeze or preserve is still edible might be difficult. Knowing how to detect whether bell peppers are sour can save you a lot of stress and anxiety.
- Eating old bell peppers might make you sick because bacteria and mold can grow on them. While it is unlikely to make you sick, you should avoid it if at all possible. A rotting pepper’s appearance is generally enough to deter you from eating it. Bell peppers that are old or rotten can cause intestinal issues.
How Do Bad Green Bell Peppers Look, Smell, Taste, and Feel?
- Your senses are the most crucial tools you have when figuring out how long bell peppers endure or when cabbage goes terrible. It’s critical to assess how a dash of pepper and other veggies feel, look, smell, and taste before deciding whether they’re safe to eat or use in a recipe.
- A similar logic applies to the shelf life of potatoes and onions. Each stage of bell pepper development is distinct, and with a bit of experience, you’ll be able to discern the difference and know what to look for in terms of spoiling.
- Green Peppers that aren’t fully ripe are complicated and lack flavor, and they’ll be bitter if you bite into them. Remember that green peppers are red, yellow, or orange peppers that have been purposefully left unripe. Therefore, it’s a good thing they’re not ripe.
- If the color of a green pepper changes, it will still be edible but will lack the green pepper flavor. The flesh of ripe bell peppers is firm, and the skin is taut and wrinkle-free. You’ll get a pleasant aroma from them as well.
- Green Bell peppers, especially red bell peppers, become sweeter as they mature. Green bell peppers retain bitterness, whereas orange and yellow bell peppers get sweeter, though not as much as red peppers. A firm, sharp, snapping sound should be produced when breaking a mature bell pepper.
- Sagging skin covers softer flesh in overripe bell peppers, and the pepper may have a sickly sweet odor from too much sugar. The flesh is likely to be bruised, and breaking it generates little to no snap. These peppers should be left at the supermarket.
How Long Do Green Peppers Last In The Fridge?
- Refrigerate your bell peppers in the crisper drawer to keep them fresh for longer. Raw Bell Peppers will last 1 to 2 weeks in the refrigerator, and cooked bell peppers have a shelf life of 3-5 days.
- When peppers get older, they develop wrinkles and have softer skin, which is frequent. These peppers can still be cooked with, but they are unappealing when eaten raw. They will get slimy, and mold will grow soon after becoming soft.
- Keep Green bell peppers in a resealable bag in the fridge’s crisper drawer for the most extended storage life. What exactly is this? Cut bell peppers should be stored in the refrigerator in an airtight container coated with a paper towel to absorb moisture. Refrigerate cooked bell peppers in an airtight container.
- Bell peppers will mostly turn from green to red, yellow, or orange when growing on the plant. Bell peppers change color and flavor as they ripen into warmer hues, becoming sweeter as they mature. When it comes to hot peppers, the same thing happens.
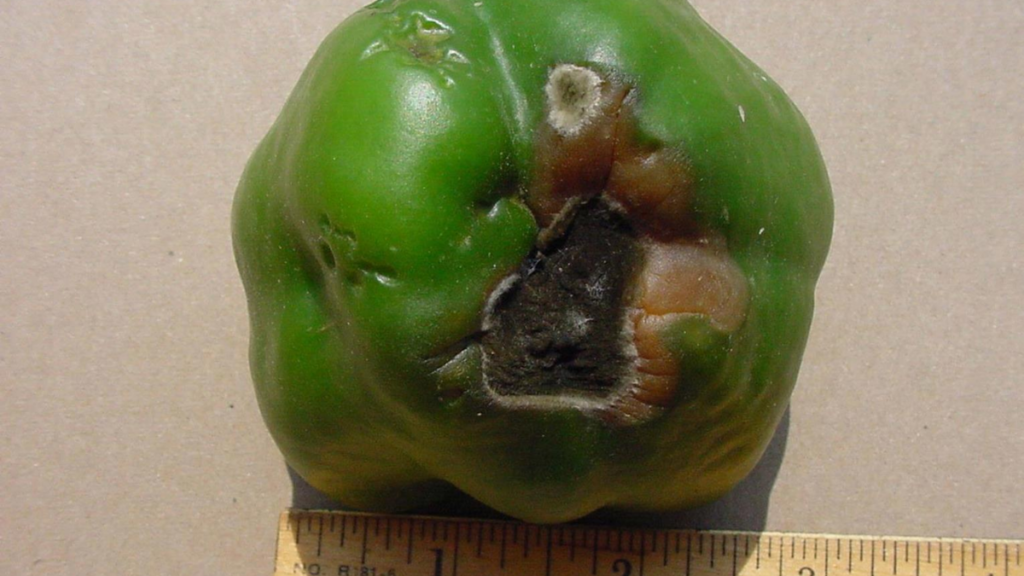
Why Do My Bell Peppers Have Brown Spots?
- The extreme heat causes the pepper tissue to break down, while the sunlight produces chemical reactions that cause tan spots on the pepper fruit’s exposed parts. This is especially prevalent in bell peppers, and in the next planting year, choosing a type with robust foliage can assist shade fruit.
- When the plant’s fruit is subjected to a combination of intense light and high temperatures, this condition develops. The extreme heat causes the pepper tissue to break down, while the sunlight produces chemical reactions that cause tan spots on the pepper fruit’s exposed parts.
- At the first indication of infection, spray with copper sulfate. Seriously diseased plants should be removed and burned, and ensure that any plant debris is removed. Bacterial stain is the last possible cause of brown leaves on a pepper plant.
- Blossom end rot is the dark, recessed area on the bottom of peppers, and it is a sign of calcium insufficiency, not a disease. It happens due to irregular watering (soil wet-dry cycles), too much nitrogen, or root injury. Peppers can be eaten with BER if the bottoms are removed.
Look for decaying indications on a bell pepper to know whether it’s terrible. The skin on the outside should be firm and dry. If there is a wrinkle, the pepper is old. Its skin will slime up, and mold will grow on it. It should have a faded appearance. Indentations will indicate rotting in the skin. It’s a red flag if your skin is dry and withered.
For several recipes, a dash of firm green bell pepper is excellent, and you’ll want to cut it with a knife. By holding the pepper up to a light and feeling its skin, you may get a sense of its texture. It’s probably too old if it feels spongy. It also has an odor, such as vinegar, that indicates it’s terrible. You should toss the skin if it is wilted, wrinkled, or yellow.
Conclusion
The skin of a bell pepper should easily peel away, and it should have a sharp feel to it. There should be some brown streaks on the interior if there is no taste. The pepper is not sour if there are no spots or brown spots. If it’s soft, however, it may be overripe. Fortunately, the hue of a bell pepper indicates when it is ripe.
To the touch, fresh bell peppers should feel solid and tight. Crisp and clear of brown stains on the stem end. Furthermore, a green bell pepper should not have dents or appear misformed when pressed. It’s probably awful if your skin is faded or wrinkled, and you won’t have to worry about the taste of decaying fruit, thankfully.