The kiwi fruit is a tiny fruit with a lot of nutritional value. Kiwifruit, also known as Chinese gooseberries, originated in China before moving to New Zealand, Europe, and eventually the United States. Unfortunately, for some people, kiwis can cause a fruit allergy. On the other hand, Kiwis are a delicious way to add vitamins, minerals, and fiber to the diet for most people who aren’t allergic. To know kiwi nutrition facts, read further.
The kiwi fruit is a versatile fruit that can be prepared in various ways. You can, for example, consume the fruit raw by cutting it into pieces or biting into it as you would an apple. Some people only eat the green slices and seeds of the fruit, but the whole thing is edible. Eating fuzzy skin can help you get three times as much fiber from the fruit. Of course, eating a kiwi raw isn’t the only way to enjoy it. You may also make a nice fruit salad by combining multiple kiwis with different fruits. Combine a few kiwi slices with other fruit, milk, or juice for a fiber-rich smoothie.
What Is Kiwi?
Kiwi is a tiny fruit about the size of an apple or an orange. But don’t be fooled by its size. Kiwis have a lot of taste and are a good source of vitamins and minerals. With its fuzzy brown skin, vibrant green color, and tiny black seeds, you can spot one in a crowd even if you’ve never eaten a kiwi.
Kiwi, also known as kiwifruit, Chinese gooseberry, or yang tao, is a fruit that originated in northern China and was traditionally used for medical purposes. Kiwi did not arrive in New Zealand until the early twentieth century and began to be cultivated there. The kiwifruit is a relatively recent fruit variety. It wasn’t until the 1940s that New Zealand began commercially growing the crop, and it wasn’t until the early 1960s that it was introduced to the United States.
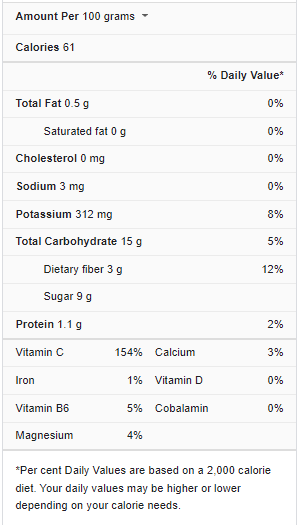
Kiwi Nutrition Facts
Carbs
One hundred grams of green kiwi has over 15 grams of carbs. Dietary fiber accounts for 3 grams of 100 grams, whereas naturally occurring sugars account for 9 grams. Kiwis have a glycemic index of 52.2, making them a low-GI fruit.
Fats
Kiwis are naturally low in fat, with 100 grams of fruit containing less than 0.5 grams of fat. Saturated fats are absent in kiwis.
Protein
One hundred grams of kiwi has almost 1.1 gram of protein, making it a minor source of amino acids.
Minerals And vitamins
One hundred grams of kiwis provide 230 percent of the daily value for vitamin C and 70% of the daily value for vitamin K. Potassium, vitamin E, and folate are all found in kiwis.
What Are The Health Benefits Of Kiwi?
1. Excellent Source Of Beneficial Plant Compounds
Kiwis are an excellent source of plant chemicals with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in the body. The antioxidant minerals vitamin C and vitamin E.Kiwis, for example, contain carotenoids, which are beneficial to one’s health. These substances include:
beta carotene lutein zeaxanthin lutein Studies have shown that Carotenoids-rich diets help protect against various diseases, including heart disease. Higher dietary consumption and blood concentrations of carotenoids, vitamin C, and vitamin E were linked to a lower risk of heart disease, total cancer, and death from all causes, according to a review of 69 studies.
Kiwis are rich in all these nutrients. Furthermore, a study including over 17,000 adults discovered that those with a diet high in total carotenoids had a lower incidence of depressive symptoms. Polyphenol chemicals found in kiwis, such as caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid, have anti-inflammatory properties in the gut and throughout the body.
2. May Benefit Heart Health
A diet high in vegetables and fruits, such as kiwis, is an excellent method to maintain heart health. According to research, eating kiwis, in particular, can help reduce heart disease risk factors such as high blood pressure. In a study, 118 patients with high normal blood pressure or stage one high blood pressure were given either kiwis or apples to eat.
When compared to individuals who ate one apple per day, those who ate three kiwis per day for eight weeks had reduced blood pressure at the end of the intervention. In a 2012 study, 102 smokers were given three kiwis every day for eight weeks. Compared to a control group, those who did this had lower blood pressure and less platelet aggregation (platelets clumping together in the blood).
Because platelets can adhere to blood vessel walls and create plaques, platelet hyperactivity may increase the risk of heart disease. Atherosclerosis is a condition that occurs when this happens. Smokers are more likely to develop plaque; thus, eating kiwis may help prevent platelet formation and lower the risk of atherosclerosis in this group. Furthermore, in specific trials, eating kiwis has been proven to lower total cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing heart-protective HDL (good) cholesterol.
3. Digestive Health
Insoluble and soluble fiber can be found in kiwis. According to studies, kiwis contain one-third soluble fiber and two-thirds insoluble fiber. The soluble fiber in kiwis may help with blood sugar balance and heart health and support good gut bacteria. In contrast, the fruit’s insoluble fiber can aid with bowel regularity.
Kiwi fiber may hold water and swell more than other fiber types, such as apple fiber and wheat bran, making it a good choice for increasing stool consistency and reducing the time food takes to pass through your digestive system. Kiwis may be suitable for persons who experience constipation because of these features.
Eating two kiwis per day for four weeks improved stool consistency and frequency and reduced straining during bowel movements, according to a study of 79 persons with chronic constipation. In addition, subjects were more satisfied with the kiwi therapy than with psyllium husk or prunes. Out of the three therapies, kiwi therapy was also associated with the lowest rate of unfavorable side effects (15).
4. Excellent Source Of Vitamin C
Vitamin C is abundant in kiwis, a nutrient that protects your cells from oxidative damage and serves various other functions in the body. According to research, eating kiwis can help you achieve adequate vitamin C levels in your blood.
In a 2012 research of 15 men with low vitamin C levels, eating one kiwi for six weeks was adequate to achieve “healthy” vitamin C levels. Eating two kiwis per day resulted in vitamin C saturation or the most significant level of vitamin C possible. Other studies have found that eating kiwis daily helps boost vitamin C levels.
Furthermore, prior research suggests that the bioavailability of vitamin C present in kiwis is comparable to that of vitamin C supplements, making kiwis a suitable supplement pill substitute. Vitamin C levels must be kept at ideal levels for the immune system to function correctly. Eating two kiwis each day for four weeks raised vitamin C levels and improved the activity of immune cells called neutrophils in young men with low vitamin C levels, according to a study.
How To Eat kiwi?
Raw kiwis are famous among many people, and they can also be used in various recipes, both sweet and savory. The majority of kiwi species should be peeled before eating. However, some species of kiwis, such as Zespri SunGold, can be eaten whole, including the peel. Kiwis can be eaten independently or added to recipes such as fruit salads.
Here Are A Few Ways To Eat Them:
- Mix sliced kiwi with berries and bananas to create a nutrient-dense fruit salad.
- Use diced kiwi in your favorite salsa recipe.
- Top smoothie bowls and Greek yogurt with sliced kiwi.
- Add fresh kiwi to smoothies and protein shakes.
- Top salads with diced kiwi for a sweet, tart twist.
- Blend kiwi into homemade salad dressings.
- Make marinades for meat and fish with blended kiwi, Worcestershire sauce, soy sauce, garlic, and olive oil.
There are many other ways to use kiwi in the kitchen. Try experimenting with kiwi in your favorite sweet and savory recipes.
Is It Healthy To Eat Kiwi Every Day?
Eating kiwi fruit is unquestionably a healthy habit to incorporate into your daily routine. Antioxidant-rich, everyday consumption could help prevent some malignancies and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. According to several scientific investigations, certain malignancies have been linked to DNA oxidation.
The kiwifruit is one of the best sources of vitamin C, vitamin K, vitamin A, carotenoids, and Omega 3 fatty acids. Because of its health benefits, everyone should consume at least one kiwi fruit per day.
What Are The Potential Health Risks Of Kiwis?
Even though kiwi is a tasty, flavorful, and usually healthful fruit, it is not for everyone. Most people are unaffected by kiwi. However, some people may be allergic to it, and symptoms may appear as soon as you bite into the luscious fruit.
Signs and symptoms of a kiwi allergy may include:
- Scratchy throat
- Swollen tongue
- Difficulty swallowing
- Vomiting
- Hives
- Tingling lips
- Sore mouth
Kiwi allergies can also affect children. If it’s the first time you’ve given your child the fruit, keep an eye on them to ensure they don’t develop any symptoms that could signal an allergic response. Symptoms can range from moderate to severe, and they may worsen the second time a youngster consumes a new meal. Difficulty breathing or loss of consciousness are signs of a severe response requiring rapid medical assistance.
In certain people, kiwifruit may help to prevent blood clots. If you have a bleeding issue, you should avoid kiwi or limit your consumption. Consult your doctor to determine how much you may consume safely. Also, before surgery, consult your doctor to determine if you should avoid eating kiwi to lessen the chance of bleeding.
Conclusion
Kiwis are a little fruit with a lovely flavor and a nutritional profile. They are high in nutrients like vitamins C and E, but studies show that they can also help you increase your intake of protective plant chemicals and improve the health of your heart and digestive system. Kiwis are also simple to prepare in the kitchen, and they go well with both sweet and savory dishes.