Coconut milk is a common addition to beverages and soups. Neither coconut water nor coconut cream is comparable. The coconut meat is grated and pressed to create coconut milk, and the resulting fatty cream is combined with water. Although high in calories, coconut milk is often only drunk in tiny amounts (just a tablespoon or two). Coconut milk can have more or less fat depending on how it is blended, much like dairy milk. Saturated fat makes up the majority of the liquid’s fat. Coconut milk is not a good source of carbohydrates, protein, or micronutrients in a typical meal.
A milky-white liquid known as coconut milk is made from grated mature coconut meat. Scientifically named Cocos nucifera, the coconut is the fruit of the coconut palm. What comes to mind if the advantages of coconut water and coconut milk are the same? The answer is no, of course. Even though they both come from coconuts and are healthy, they are two different liquids.
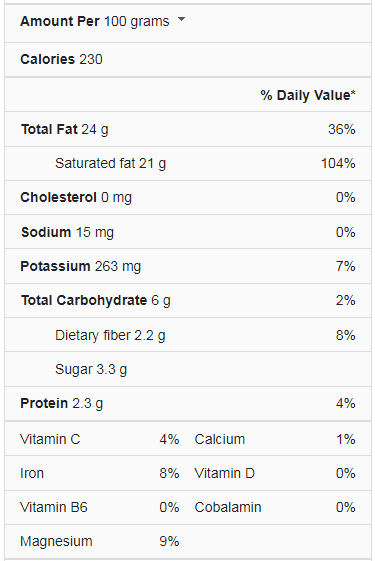
Coconut Milk Nutrition Facts
What is Exactly Coconut Milk?
The mature brown coconuts, the fruit of the coconut tree, contain white flesh that is used to make coconut milk. The milk has a rich, creamy texture and a thick consistency.
This milk is frequently used in Southeast Asian cuisines like Thai. It is also well-liked there with Hawaii, India, and a few South American and Caribbean nations. Coconut water, naturally present in young, green coconuts, should not be confused with coconut milk.
The milk does not spontaneously occur as coconut water does. Instead, coconut milk, which contains roughly 50% water, is made by combining solid coconut meat with water. Coconut water, in comparison, contains roughly 94 percent water. Compared to coconut milk, it has far less fat and fewer nutrients.
How is it Made?
Coconut milk is classified as either thick or thin based on consistency and how much it’s processed.
- Thick: Solid coconut flesh is finely grated and boiled or simmered in water. The mixture is then strained through cheesecloth to produce thick coconut milk.
- Thin: After making thick coconut milk, the grated coconut remaining in the cheesecloth is simmered in water. The straining process is then repeated to produce thin milk.
In traditional cuisines, thick coconut milk is used in desserts and thick sauces, and thin milk is used in soups and thin sauces. Most canned coconut milk contains a combination of thin and thick milk. It’s also very easy to make your coconut milk at home, adjusting the thickness to your liking.
What are the Health Benefits of Coconut Milk?
Here are the health benefits of coconut milk:
It Aids in Weight Loss
Short and medium-chain triglycerides, regarded as beneficial fats, are abundant in coconut milk. They make you feel fuller for longer, making you eat less and preventing you from giving in to cravings. Additionally, compared to longer chain fatty acids, they are more likely to be turned into energy. These are primarily stored within the body, which contributes to obesity.
It Contains Antioxidants
Vitamins C and E, widely known for their antioxidant effects, are abundant in coconut milk. Our bodily tissues produce free oxygen radicals from metabolism, damaging biological components, speeding up aging, and promoting tumors’ development. Coconut milk’s antioxidants aid in scavenging these dangerous chemicals.
Electrolyte Balance
Electrolytes like potassium, magnesium, and phosphorus are abundant in coconut milk. For preserving a proper cardiac rhythm, potassium is crucial, and the proper functioning of healthy muscles also depends on it. Magnesium is necessary for typical neuron and muscle function and a strong immune system. A crucial part of the structure of bones and teeth is phosphorus. You may ensure that the body has enough phosphorous to meet these requirements by including coconut milk in your recipes.
Prevents Heart Disease
It is well known that coconut milk raises the body’s HDL cholesterol levels. According to recent scientific studies, if drunk in moderation, coconut milk may help lower the body’s LDL cholesterol levels (bad cholesterol).
Endothelium, or the lining of blood vessels, is safeguarded by the anti-inflammatory characteristics of HDL cholesterol. On the other hand, LDL cholesterol encourages the growth of plaques in blood arteries, which leads to pathological constriction. Heart attacks can happen when the blood arteries that supply the heart muscles are constricted.
Strengthens the Immune System
Lauric acid, known for its antibacterial qualities, is present in coconut milk and supports the body’s defenses against bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. According to a study conducted in the Philippines, children with pneumonia responded more quickly to treatment with coconut milk plus antibiotics than those who received only antibiotics.
Prevention of Anemia
Iron is in substantial amounts in coconut milk, which is crucial for producing healthy red blood cells with adequate hemoglobin levels. Coconut milk will aid in preventing anemia, which is frequently brought on by a diet low in iron.
Healthy Hair and Skin
The usage of coconut milk as a conditioning treatment for healthy hair has recently grown in favor. Its high-fat content functions as a moisture-retention sealant. Coconut milk can be applied to the scalp to lessen dandruff and itching. This is because lauric acid, which has antibacterial and antifungal effects, is included.
When administered topically to the skin, coconut milk aids in maintaining the skin’s suppleness. This significantly slows down the creation of wrinkles, making you look younger. It is claimed that its antimicrobial characteristics help prevent acne. These days, women worldwide use this lotion to remove their makeup.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Joint discomfort and inflammation can be reduced with coconut milk. It’s well known that sugar causes inflammation. For people with autoimmune inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and lupus arthritis, substituting it for coconut milk as a sweetener can have astonishing results.
Potential Side Effects
Although coconut milk has a lot of many health benefits, it has some potential side effects also:
- The milk is unlikely to have negative consequences unless you have a coconut allergy, and coconut allergies are not as common as allergies to tree nuts and peanuts.
- However, some specialists in gastrointestinal disorders advise patients with a FODMAP intolerance to consume no more than 1/2 cup (120 ml) of coconut milk at a time.
- Additionally, many canned types include bisphenol A (BPA), a substance that can seep into food through can linings. BPA has been linked in animal and human studies to cancer and issues with reproduction.
- It is noteworthy that certain companies employ BPA-free packaging, which is advised if you decide to eat canned coconut milk.
How to Use it?
Although coconut milk is nutritious, it’s also high in calories. Keep this in mind when adding it to foods or using it in recipes.
Ideas for Adding it to your Diet
- Include a couple of tablespoons (30–60 ml) in your coffee.
- Add half a cup (120 ml) to a smoothie or protein shake.
- Pour a small amount over berries or sliced papaya.
- Add a few tablespoons (30–60 ml) to oatmeal or other cooked cereal.
How to Select the Best Coconut Milk?
Here are a few tips for selecting the best coconut milk:
- Read the label: Whenever possible, choose a product that contains only coconut and water.
- Choose BPA-free cans: Purchase coconut milk from companies that use BPA-free cans, such as Native Forest and Natural Value.
- Use cartons: Unsweetened coconut milk usually contains less fat and fewer calories than canned options.
- Go light: For a lower-calorie option, select light canned coconut milk. It’s thinner and contains about 125 calories per 1/2 cup (120 ml).
- Make your own: For the freshest, healthiest coconut milk, make your own by blending 1.5–2 cups (355–470 ml) of unsweetened shredded coconut with 4 cups of hot water, then strain through a cheesecloth.
How to Store Coconut Milk?
You can either prepare fresh coconut milk at home or buy it in a carton or can at the supermarket. Removing any remaining coconut milk is unnecessary because recipes frequently call for less coconut milk than an entire can. The following three food preservation strategies will help coconut milk stay fresh longer:
At Room Temperature
Coconut milk can be kept at room temperature for several months if it hasn’t been opened. Canning coconut milk should be kept in a cold, dark area like a pantry or cabinet for optimal results. Some coconut milk cartons are also shelf-stable so that they can be kept for a while or until the expiration date is reached by keeping them in a cold, dark place.
In the Refrigerator
It is certainly not shelf-stable if you buy a carton of coconut milk from the refrigerated department of a grocery store. Use coconut milk within seven to ten days of opening the carton, and keep the carton in the refrigerator until the indicated expiration date. Use any remaining canned coconut milk within five days and store it in a glass jar or other airtight container in the refrigerator.
In the Freezer
To store coconut milk for a long time, it can be frozen. Remember that frozen coconut milk will have a gritty texture when defrosted and lose some of its flavors. To freeze coconut milk, split it according to a recipe and place it in separate plastic freezer bags. Until they are frozen, place the bags flat in the freezer. Place a bag of coconut milk in the fridge overnight to defrost. Coconut milk can also be frozen in ice cube trays as an alternative. Coconut milk frozen cubes can be added to smoothies or defrosted and used directly in soups, stews, or Thai curries.
Conclusion
A delightful, wholesome, and adaptable food commonly available is coconut milk. It is also simple to make at home. It is rich in essential nutrients, including copper and manganese. A moderate amount in your diet may improve your heart health and have additional advantages. An opaque, white liquid called coconut milk is made from the meat of a ripe coconut.
Grated coconut meat is combined with hot water and pressed through a cheesecloth to create coconut milk the traditional way. A rich, fatty liquid known as coconut cream is produced by this method. You can refine coconut cream further to create coconut oil or crush it once more to create coconut milk. Coconut milk that has been industrially processed and is available in cans at the grocery store is mechanically grated, squeezed, and frequently stabilized with guar gum.