Eggs are among the best sources of a wide variety of nutrients. They have a wide variety of nutritional benefits, but they’re also easy to prepare, having a nutritious, portable breakfast in minutes. When cooked thoroughly, eggs are much less likely to contain harmful bacteria that can cause illness. Here’s a look at the hard-boiled egg nutrition facts with the yolk. A hard-boiled egg is a healthier choice than a raw or undercooked egg, but you can’t beat the convenience of a quick meal on the go.
The best way to determine whether an egg is a good choice for your diet is to check the nutritional facts. Although most of the nutrients in eggs are concentrated in the yolk, you can also check the nutritional value by looking at the egg whites, which contain many proteins and essential nutrients. In addition to protein, eggs are also rich sources of several vitamins and minerals. For example, eggs contain vitamin D, which requires a lot of fat to be absorbed into the body. Additionally, egg yolks contain all of the amino acids you need.
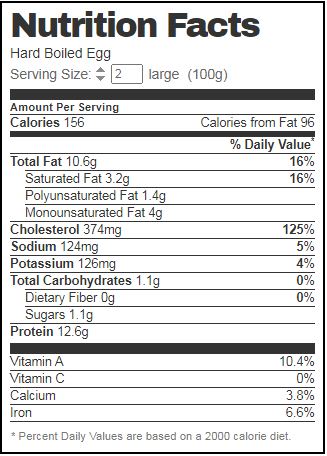
Hard Boil Egg Nutrition Facts
What is a Hard-Boiled Egg?
Boiled eggs are eggs that have been cooked in their shells, usually by immersing them in boiling water. Hard-boiled eggs are cooked when the egg white and yolk both solidify, whereas soft-boiled eggs may leave the yolk and occasionally the white partially liquid and uncooked. Around the world, boiled eggs are a popular breakfast item.
Boiling eggs can be done in various ways, including immersion in boiling water. Eggs can also be coddled or steamed at a temperature below that of boiling water. The egg timer got its name because it was often used to time the cooking of eggs.
What are the Health Benefits of Hard-Boiled Egg?
They’re delicious, filling, and beneficial to your health. Here are some examples of hard-boiled egg health advantages.
- Hard-boiled eggs are a great source of lean protein. They’ll keep you satiated without consuming too many calories, which is beneficial if you’re trying to reduce weight.
- In addition to vitamin D, the protein in hard-boiled eggs helps to enhance fetal development. These nutrients help your baby’s teeth, bones, and overall growth during pregnancy.
- Egg whites that have been boiled are healthier than those cooked in other ways. Remove the yolks after cooking to enjoy a low-cholesterol snack.
- Choline is essential for cellular growth and maintenance, and hard-boiled eggs are the most common source in the American diet.
- The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities of lutein and zeaxanthin, which are contained in boiled eggs, aid in maintaining eye health.
- Hard-boiled eggs’ combination of nutritious ingredients like protein and choline helps wake up your brain, especially after breakfast.
Cholesterol is High, But it does Not Increase the Risk of Heart Disease Why?
Eggs have acquired a poor rap due to their high cholesterol level. Eggs have a lot of cholesterol, and one big hard-boiled egg contains 373 mg of cholesterol, or 71% of the recommended daily allowance. Recent research, however, indicates that dietary cholesterol has only a minor impact on blood cholesterol levels. Dietary cholesterol is not linked to an increased risk of heart disease in most people, and it does not raise total cholesterol or “bad” LDL cholesterol levels.
Eating eggs may help you get more “good” HDL cholesterol. Furthermore, eating one whole egg per day was not connected to an increased risk of heart disease in two studies, including over 100,000 healthy adults. People with diabetes, on the other hand, should be cautious while eating eggs, as some evidence suggests that eating seven eggs per week may raise the risk of heart disease.
Finally, more research into the link between egg consumption and the risk of heart disease in people with diabetes is required.
Hard-Boiled vs. Fried
To make hard-boiled eggs, place unshelled eggs in a saucepan filled with cold water and cook until the yolk solidifies. They are prepared without the addition of any additional butter or oil. On the other hand, Fried eggs necessitate the addition of more butter or oil, which adds calories and fat. Apart from the fat and calorie content, hard-boiled and fried eggs’ vitamin and mineral profiles are relatively comparable, and they are identical in terms of protein and nutritional content.
Unlike hard-boiled eggs, which may be made without any additional ingredients, fried eggs require added butter or oil, which increases their calorie content. However, in terms of micronutrients, fried and boiled eggs are relatively similar.
What’s Better: Egg White or Egg Yolk?
The finest way to start your mornings is with eggs. The nutrient-dense eggs have a slew of health advantages. They’re high in protein, vitamins, and good fats. Our everyday breakfast usually consists of omelets, scrambled eggs, or boiled eggs. They’re used in a variety of salads and main courses. They are useful to the body regardless of how they are consumed.
A well-balanced diet will always contain a significant amount of this superfood. It contains all the vital proteins, vitamins, and minerals that one cannot afford to be without. However, the age-old question of which section of an egg is healthier has remained unresolved. Is it the egg white or the yolk that is better than the other? Let’s have a look at it.
Egg Yolks
For many years, egg yolks have been avoided because they contain saturated fat and dietary cholesterol, raising cholesterol levels in the body and making it more susceptible to heart disease. The most important fact is that egg yolks contain more nutrients than egg whites.
Yes, you read that correctly. The nutritional value of the golden section of an egg is substantially higher. Vitamin B6, B12, A, D, E, and K are among the vital components. Calcium, magnesium, iron, and selenium are all abundant in it. The carotenoids found in the yolk aid with visual improvement. These carotenoids are antioxidants that protect the eyes from free radicals that cause retinal damage. Choline, a water-soluble nutrient found in egg yolks, has anti-inflammatory qualities and regulates the body’s circulatory function.
Egg White
The albumen, often known as the egg white, is the exterior layer of an egg. Because it is fat-free and low in calories, most health-conscious people prefer to eat only this portion. It provides the body with vital proteins without adding unnecessary calories. It is well-known for its potential to aid muscle growth and weight development, and it can also keep you satisfied for a longer time. The potassium mineral found in egg whites can aid in the reduction and maintenance of blood pressure. Vitamin riboflavin aids in the prevention of cataracts and migraines.
Verdict
The yolk holds 93 percent of the iron in an entire egg, whereas the white has 7%. The yolk contains 90% of the calcium in the body. While both egg sections are healthful, the yolks appear to be more advantageous in terms of vitamin content. They should be consumed in moderation because they contain cholesterol, which might increase the risk of diseases. So, before tossing them out the next time you have eggs, consider that you may be wasting a lot of nutrients.
It’s also possible to eat whole eggs. In this manner, you obtain all nutrients while also reaping the health advantages.
Conclusion
Eggs are generally thought to be healthy because they contain a high amount of good HDL cholesterol (HDL), which helps to reduce the risk of stroke and heart disease. As a result, if you eat an egg every day, you won’t have to be concerned about your cholesterol levels. You’ll savor the entire egg’s flavor, and you can even add vegetables for more flavor. The American Heart Association recommended that everyone consume one egg per day, regardless of their risk factors.
When picking hard-boiled eggs, ensure the yolks are completely cooked before serving. Egg whites are significantly more nutritious than egg yolks, so if you don’t like the yolk, there are many other high-quality protein sources. To gain the nutrition benefits of eggs, try quinoa, beans, and fish. The flavor and texture will delight you, and you’ll be happy you did!
Hard-boiled eggs, despite their negative reputation, are a highly healthy source of protein. All nine necessary amino acids are found in them. Modest egg-eating does not raise cholesterol levels in healthy people. Consult your doctor before introducing eggs to your diet if you’re unsure about their nutritional value. Hard-boiled eggs can be stored without their shells for up to a week, but they must be consumed daily.