With so many cooking oils on the market, it’s challenging to determine which ones are healthier. Peanut oil is a popular cooking oil frequently used, particularly when frying meals. Peanut oil, on the other hand, has numerous health benefits. This oil is high in vitamin E, an antioxidant with several health benefits, including protection against chronic disease. Because of this and its healthy fat content, it can benefit your diet if consumed in moderation.
Peanut oil is a sweet, nutty, and fragrant organic edible oil made by pressing peanut kernels. Peanuts are thought to have originated in Central America, from where Spanish explorers disseminated them to other areas of the world. Peanut crops are now widely grown as important oilseeds commercially in China, India, Africa, and the United States of America.
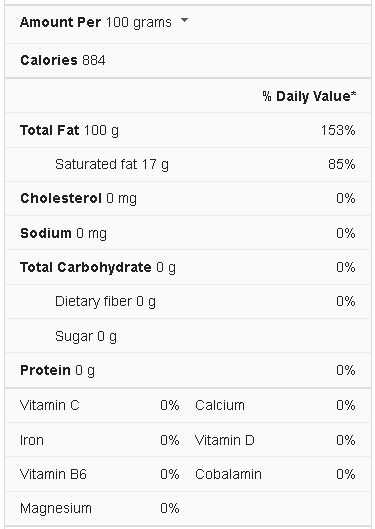
Peanut Oil Nutrition Facts
What is Peanut Oil?
Peanut oil is a vegetable-derived oil prepared from the edible seeds of the peanut plant. It is also known as groundnut oil or Arachis oil. Even though the peanut plant flowers are above ground, the seeds or peanuts grow underground. Peanuts are also called groundnuts because of this. Peanuts are frequently confused with tree nuts such as walnuts and almonds, but they are a pea and bean family legume. Peanut oil can have a variety of flavors, ranging from mild and sweet to robust and nutty, depending on how it is processed.
There are several different types of peanut oil. Each one is made using different techniques:
Refined Peanut Pil: This variety has been purified, bleached, and deodorized, removing the oil’s allergenic components. It is usually safe for people who are allergic to peanuts. Restaurants frequently utilize it to fry meals like chicken and french fries.
Cold-Pressed Peanut Oil: Peanuts are crushed in this procedure to extract the oil. This low-heat method preserves the natural peanut flavor and more nutrients than refining.
Gourmet Peanut Oil: This oil, considered a specialty oil, is unrefined and frequently roasted, giving it a richer, more robust flavor than refined oil. It’s used to give meals like stir-fries a robust, nutty flavor.
Peanut Oil Blends: Peanut oil is frequently mixed with soybean oil, with a similar flavor but less expensive. Consumers will find this variety more inexpensive, and it is typically supplied in quantity for frying dishes.
Peanut oil is used worldwide, but it is trendy in Chinese, South Asian, and Southeast Asian cuisines. During World War II, when other oils were rare due to food shortages, they became more popular in the United States. It is often used to fry dishes and has a high smoke point of 437°F (225°C).
Is Peanut Oil Good for your Health?
The best health advantages of Peanut Oil are listed here. This oil can be used for cooking, medicine, and nutrition, among other things. Let’s look at how peanut oil can be used in various ways. We also learned about its history and cultivation.
Peanut Oil Used for Body Massage Therapy
Peanut Oil Helps in Improving Heart Health
Because of the fatty acid concentration, peanut oil has a high-calorie load. On the other hand, this oil is high in mono-unsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), which help lower bad cholesterol while raising good cholesterol in the blood. Peanut oil is beneficial to heart patients because it helps maintain a healthy blood lipid profile, which helps prevent coronary artery disease and heart attacks.
Peanut Oil Helps in Improving Blood Flow
Linoleic acid, found in peanut oil, is a precursor to prostaglandins. Prostaglandin is essential for various critical bodily processes, including the contraction and dilatation of blood vessels and other muscles.
Peanut Oil Maintains Cholesterol Level
To maintain normal cholesterol levels and heart health, we should reasonably consume peanut cooking oil in our regular diet.
Peanut Oil Helps in Lowering High Blood Pressure
Peanut oil is substantial in monounsaturated fats, which help to decrease blood pressure. This helps to minimize the risk of heart disease indirectly.
Native Harvest Expeller Pressed Non-GMO Peanut Oil
Features:
- Native Harvest’s 100% Pure High Heat Refined, NON-GMO Peanut Oil provides allergen-free monounsaturated fats. Peanut oil is high in monounsaturated “good” fat and low in saturated “bad” fat. And also a source of antioxidants, vitamin E, and phytosterols, which are believed to help keep lower cholesterol.
- Native Harvest’s Peanut Oil brings a nutty flavor, an excellent complement to traditional Asian and African food recipes.
- Our Peanut Oil is perfect for healthier frying because it can be heated to a higher temperature than most other oils. Asian and African food recipes typically use high heat, and because refined peanut oil has a high smoke point, it can tolerate most style dishes.
- We naturally expeller pressed our NON-GMO Peanut Oil without harmful chemicals for delicate flavor and better-tasting food.
- Peanut oil is widely used in aromatherapy since it has a very light and nutty aroma. This can be used for body massage for a relaxing and rejuvenating experience.
How to Use Peanut Oil?
Peanut oil can be used for frying, sautéing, or just seasoning. Although most types of peanut oil have a light, neutral flavor, they can occasionally have a nutty flavor. Roasted peanut oils have a strong flavor and are generally added after the food has been cooked.
One of the main reasons peanut oil is used as frying oil is its high smoke point, and food cooks quickly at high temperatures, producing a crispy crust with minimal oil absorption. Although raw peanut oil smells nutty, refined peanut oil is odorless.
Peanut oil has a high concentration of monounsaturated “healthy” fat and a low concentration of saturated “bad” fat. This is thought to aid in the prevention of heart disease and the reduction of cholesterol. Peanut oil may assist in the reduction of fatty buildup in blood vessels.
Does Peanut Oil also Go Bad?
Oils deteriorate as they age, but not in the same manner that other foods do. You won’t see visible indications like mold or a change in texture with oil, but they are more subtle. One early warning sign of old peanut oil is that it will not taste as tasty as you think when you cook or fry with it. When peanut oil starts to go wrong, the clarity and color of the oil will alter, and it will get darker. You’ll also notice that it has an unusual odor. As a result, if you see these changes, it’s time to get rid of the oil.
What are the Side Effects of Peanut Oil?
Here are some side effects also of using peanut oil:
- Peanut allergies are among the most frequent in youngsters. A peanut allergy can cause severe reactions, including anaphylaxis and death. On the other hand, Peanut oil isn’t known to trigger the same severe allergic reaction.
- Peanut oil’s omega-6 fatty acids can be detrimental if you consume too much of this type of fat in your diet. Many Americans currently eat a diet rich in omega-6 fats, found in vegetable oils, fast food, and various packaged foods.
- Furthermore, while pregnant or breastfeeding, women should consume average amounts of peanut oil.
- However, it has been noted that this oil might induce primary allergic responses in those who are hypersensitive to peanuts, soybeans, and other leguminous plants.
- Another severe and potentially fatal side effect of peanut oil is anaphylaxis. If a person with a peanut allergy unknowingly ingests or uses peanut oil, severe adverse symptoms such as vomiting, abdominal pain, swollen lips and throat, difficulty breathing, and chest congestion may occur.
Conclusion
Peanut oil is popular cooking oil because of its nutty, mild flavor, and high smoke point. It could provide several health benefits. It has been associated with lower rates of cardiovascular disease, reduced blood sugar in diabetics, and tumor growth in cancer patients. Peanut oil, however, is abundant in omega-6 fatty acids, which can be detrimental if ingested in large amounts, and it’s also susceptible to oxidation.
While peanut oil is not classified as an allergy by health authorities, those with peanut allergies should consult an allergist before drinking it. With so many alternative healthy fat options on the market, it might be good to go with oil that provides more benefits while posing fewer health dangers.