Minerals including iron, magnesium, and zinc are abundant in dark chocolate. Flavonoids, another type of antioxidant found in cocoa and dark chocolate, may provide several health advantages. Cacao is a plant with a lot of nutrients and antioxidants that are used to make chocolate. Sugar, milk, cocoa butter, and small amounts of cacao are the main ingredients of commercial milk chocolate. Dark chocolate, in comparison, has significantly more cacao and less sugar than milk chocolate.
Chocolate labeled “dark chocolate” must contain at least 50% cocoa solids, cocoa butter, and sugar; unlike milk chocolate, which may contain trace amounts of milk due to production cross-contamination, dark chocolate does not. The more cocoa solids you consume and the greater the potential health benefits, the darker the chocolate.
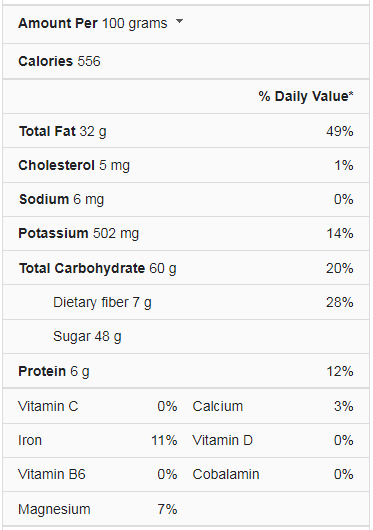
Dark Chocolate Bars Nutrition Facts
Facts Related to Dark Chocolate Bar
Here are some important facts related to dark chocolate bars:
- Their dietary usage in preserving cardiovascular health is supported by prior research on plant sterols (PS) and cocoa flavanols (CF).
- In a population with increased serum cholesterol, this double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial examined the effects of daily ingestion of a dark chocolate bar with additional PS on serum lipids, blood pressure, and other circulating cardiovascular health markers.
- With blood pressure of 159/99 mm Hg and serum total cholesterol values of 5.20–7.28 mmol/L, we recruited 49 persons (32 women and 17 men). Participants were randomly divided into two groups after a 2-week lead-in using the AHA-style diet and told to eat 2 bars of dark chocolate with cocoa flavanols per day, either with PS (1.1 g per bar) or without PS. Each 419-kJ bar had a matching amount of nutrients and about 180 mg of CF.
- Participants ate 1 bar twice daily for four weeks before switching to the other for another four weeks. At baseline, 4 and 8 weeks later, other cardiovascular markers were also assessed in the serum. Every two weeks, blood pressure was taken.
- Regular eating of the PS-containing chocolate bar reduced serum total and LDL cholesterol by 2.0 and 5.3 percent, respectively (P 0.05). Systolic blood pressure was similarly decreased by CF consumption at eight weeks (by 5.8 mm Hg; P 0.05). The results of a low-fat diet show that regular chocolate bars containing PS and CF may enhance cardiovascular health by reducing cholesterol and elevating blood pressure.
What is Dark Chocolate Bar?
Dark chocolate is chocolate that doesn’t have any additional milk solids. Cacao beans, sugar, an emulsifier such as soy lecithin to maintain texture, and flavorings like vanilla make up the basic ingredients. Dark chocolate tastes harsh and has higher cocoa and lower sugar content; a small amount is considered a healthy snack. Its flavor makes it a favorite kind of chocolate for melting and baking a range of sweets.
It can be difficult to settle for any other type of chocolate if you enjoy dark chocolate. These dark chocolate bars are adored for their delectably rich flavor, which combines bitter and sweet flavors. In addition to tasting good, some people even frequently drink dark chocolate due to its numerous health advantages.
What are the Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate?
Here are the health benefits of dark chocolate:
Chocolate Prevents Cardiovascular Diseases
The main cause of death worldwide is cardiovascular disease (CVD), and high blood pressure and cholesterol levels are the most typical risk factors for this illness. According to some epidemiological studies, fruits and vegetables are great for preventing CVD because they are high in flavonoids. Similarly, cacao’s high flavonoid content has lowered the risk of CVD.
The Stockholm Heart Epidemiology Program investigated the long-term consequences of dark chocolate consumption. According to the study, those who drink dark chocolate have a lower cardiac mortality rate than those who have never tried it. Thus, it is hypothesized that flavanols act as cardioprotective agents when present in sufficient quantities, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Chocolate Lowers Blood Pressure
The Harvard School of Public Study’s observational investigation supports blood pressure and cacao association. It discusses the medicinal properties (flavonoids) of dark chocolate, which has a 50–70% cocoa content and is useful for decreasing blood pressure.
Nitric Oxide production by the endothelium, the thin membrane that lines the inside of the heart and blood vessels and regulates vascular contraction and relaxation, is also aided by flavonoids. Nitric oxide is released, dilating blood vessels, boosting blood flow, and lowering blood pressure. As a result, it may be a simple and efficient component that helps hypertensive individuals control their blood pressure.
Chocolate Resists Cell Damage
Antioxidants are abundant in dark chocolate, which guards against tissue damage from free radicals. Free radicals are chemical species the body produces as a byproduct of its metabolism when under stress, which causes the body to pump more blood.
However, issues can arise if free radical levels are persistently raised. Antioxidants shield cells from cellular harm and counteract the effects of free radicals. Additionally, it helps treat conditions including Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
Chocolate Treats Depression
Dark chocolate is connected to a lower risk of depression and the pleasure it brings when consumed. It has been shown that persons who consume 24 grams or less of dark chocolate each day may have antidepressant benefits.
The combination of flavonoids, known to elevate mood, theobromine, which provides energy, N-acylethanolamines, a fatty acid with euphoric properties, and phenylethylamine can alleviate depression (triggers dopamine).
Chocolate Works Against Diabetes
Polyphenols, a naturally occurring substance with antioxidant qualities that reduce insulin resistance, are found in dark chocolate. People with Type 2 diabetes may benefit from this regarding blood sugar management. Additionally, a study published in the journal Appetite shows that participants who infrequently ate dark chocolate had a much higher chance of acquiring diabetes in the following five years than those who ate dark chocolate at least once a week.
Chocolate Aids Weight Loss
Dark chocolate can aid in weight loss when consumed in moderation. It contains monounsaturated fatty acids, which enhance metabolism and hasten calorie burning. Additionally, eating dark chocolate 20 minutes before a meal reduces cravings. Strangely, dark chocolate’s magnesium and antioxidants help ease pain, motivating people to exercise. This may be an additional benefit for those having trouble losing weight.
Side Effects & Precautions
- A 1-ounce serving of dark chocolate with 70% cocoa provides about 20-25 mg caffeine. Excessive consumption of dark chocolate can increase caffeine levels in the blood, causing increased heart rate, nausea, dehydration and insomnia.
- Approximately 30-60 grams of dark chocolate per day is recommended quantity to be healthy. Also, people having diabetes can consult their doctor before planning to consume daily.
Precautions
- Pregnancy- Dark chocolate can be consumed in moderation. Eating excessive dark chocolate can increase caffeine intake, which can be unsafe for the fetus. Higher caffeine content can cause issues like premature delivery, low birth weight, and even miscarriage. It is better to watch the quantity of your consumption. Consult a doctor and abide by the suggested quantity.
- Breastfeeding- Mothers breastfeeding infants must be careful about their Dark Chocolate consumption. The caffeine in dark chocolate can transfer from the mother to the nursing baby and cause insomnia, restlessness and even rashes.
- Bleeding Disorders- Consuming a lot of dark chocolate can also lead to the risk of slowing down the blood clotting process. It can be dangerous for people who have bleeding disorders or hemophilia.
- Palpitation- The cocoa present in Dark Chocolate can increase pulse rate and spike blood pressure if consumed in a rather large quantity
How to Use Dark Chocolate?
Dark chocolate of 70% or more does contain the most beneficial flavanols, but the darker it gets, the more bitter it tastes.
Dark chocolate is common in baking, and you’ll often find it in recipes for treats like:
When baking with dark chocolate, it’s important to heat it slowly over low stove heat or at 50% power on your microwave, so you don’t scorch it.
Here are a few other ideas for incorporating small servings of dark chocolate into your diet:
- Serve a few small squares of dark chocolate with fresh fruit for a simple dessert.
- Stir some melted dark chocolate into a warm bowl of oatmeal.
- Add a tablespoon or two of dark chocolate to a frozen banana, and blend them to create a tasty no-dairy substitute for chocolate ice cream.
How to Store Dark Chocolate?
Dark chocolate should be kept in a cool and dark cabinet and away from heat sources like the stove, fridge, or other appliances. Excess chocolate should be wrapped in its opened packaging, then covered with plastic wrap or put in an airtight container to keep moisture out. Dark chocolate can last for one or two years when stored properly. It doesn’t need to be refrigerated unless your kitchen is hot; in that case, it will last for three to six months. Because chocolate can absorb flavors from other foods, be sure it is tightly sealed.
As a result of the sugar rising to the surface, moisture can also cause chocolate to “bloom,” resulting in a white, powdery, or streaky surface. It may not be of the same quality, flavor, or texture, but it is still edible and frequently best used for melting.
Conclusion
Dark chocolate has less sugar than milk chocolate and is a great source of minerals and antioxidants.
According to several studies, dark chocolate may help reduce the risk of heart disease, inflammation and insulin resistance and boost brain function and the diversity of the gut microbiota.
There is a lot of data to support cocoa’s full health advantages, including its ability to prevent heart disease. Dark chocolate is heavy in fat and calories, so those who want to include it in their diet should use moderation.
Although sugar is normally present in dark chocolates in minute amounts, the darker the chocolate, the less sugar it will typically contain. One of the rare foods that taste great and has a lot to offer in terms of health is chocolate.