According to the American Heart Association, fish should be eaten twice a week, and this is due to the high protein and omega-3 fatty acid content of fish and its low saturated fat content. Eating fish can also help you get enough vitamin D in your body. While the prospect of cooking fish daunts some individuals, numerous straightforward methods are available. When choosing a preparation method, choose one that preserves the nutritional value of your fish. There are numerous options available.
Fish has traditionally been a nutritious food, not to mention how adaptive and versatile it is. Fish can be cooked in various ways, including baking, grilling, steaming, frying, and poaching. It’s quite simple to prepare, and there are countless possibilities for creating delicious recipes with it.
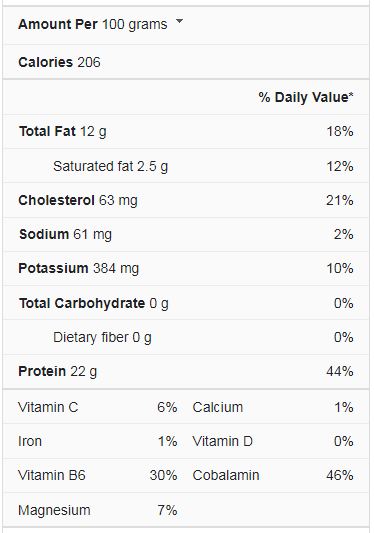
Fish Nutrition Facts
What is Exactly Fish as Food?
Humans catch and eat a wide variety of fish species in practically every part of the globe. Fish has been a significant source of protein and other nutrients throughout history.
Like other animals (such as pig vs. pork) or other languages, English does not have a specific culinary word for cuisine derived from fish (Spanish Pescado). Fish may include so-called shellfish such as mollusks, crabs, and echinoderms in culinary and fisheries contexts; more broadly, seafood includes both fish and other marine life utilized as food.
Choosing Which Fish to Cook?
Each variety of fish has its own set of nutritional benefits. Salmon, for example, is high in vitamin D and all of the B vitamins. Calcium is also found in canned salmon. Phosphorus, zinc, selenium, and B-vitamins are all found in tuna. These alternatives and herring, halibut, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids. Eating a variety of fish meets more of your body’s nutritional needs.
Small children, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and anyone who is pregnant or breastfeeding should avoid mercury-rich fish, according to the US Food and Drug Administration. This is because mercury harms the brain and neurological system of a fetus or a young child.
How to Cook a Fish?
Consider the cooking method that best suits the fat level of the fish when deciding how to prepare it. In other words, lean fish tastes best when cooked in a wet-cooking method like poaching or steaming. While fish with a greater fat content will often have the best flavor when prepared using dry-cooking methods such as grilling or baking, fish with a lower fat content will often have the best flavor when prepared using wet-cooking methods such as baking or grilling. Wet or dry methods can prepare fish with a moderate-fat level. Here are different types of methods for cooking a fish:
Poach or Steam Fish
Water, lemon juice, garlic, onions, proper fish seasoning, and spices are the simplest ways to poach fish. Cook the fish for 10 minutes, or until the center of the fish is opaque and flakes readily with a fork, after bringing the mixture to a simmer over medium heat. Keep the liquid at a low simmer rather than bringing it to a boil.
When steaming whole fish, fill a stockpot halfway with water and place a steamer on the stockpot’s rim. Place the fish in the steamer, cover, and steam for 8 minutes, or until the fish easily flakes with a fork.
Baking a Fish
If you want to bake fish in the oven, keep in mind that the temperature and time will vary depending on the thickness of the fillets. Most fish is baked uncovered for 15 to 20 minutes at 350°F or until it flakes readily with a fork. To add flavor to your recipe, sprinkle the fillets with a lemon-butter sauce or use some of the best herbs for fish (rosemary, oregano, basil).
Grilling a Fish
Place the fillets in a fish basket on the grill rack, directly over the coals (you can add herbs for fish or other fish seasonings). Grill for 6 to 8 minutes on the first side, then flip and cook for 3 to 8 minutes on the second side, or until the salmon is opaque. Cooking time will be determined by the thickness of the fillets. Make a small cut in the thickest portion of the fillet to see if the fish is completely cooked (opaque).
Frying a Fish
Use a large, heavy skillet and vegetable oil or shortening to pan-fry salmon. Over medium-high heat, heat the oil or shortening. Dip each fillet into the egg mixture first, covering both sides. After that, gently push the fillet into the cornmeal mixture to help it cling to the fish. Repeat with each fillet until the entire fillet is covered in cornmeal. Fry the fish on one side until golden brown (3 to 4 minutes), then flip and fry the other side.
Microwaving
Microwave ovens use energy waves for cooking food, and these waves cause some of the molecules in the food to vibrate, causing the food to heat up. Some individuals believe that cooking with a microwave reduces the nutrients in food; hence, this cooking method may be contentious.
On the other hand, microwaving is a quick and low-temperature cooking procedure. As a result, it can maintain some nutrients better than other cooking methods. Numerous studies have shown microwaving fish to help reduce the loss of beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
Sous Vide
The term “sous vide” means “under vacuum” in French. Food is placed within a sealed pouch and cooked in a temperature-controlled water bath in this cooking process. It’s a low-temperature cooking technique in which food is cooked slowly over a lengthy period at a low temperature. Although sous vide cooking takes a long time, it’s deemed a healthy cooking method since it uses a closely controlled, very low temperature to lock in moisture and nutrients. According to one study, cooked salmon sous vide maintained more omega-3 fatty acids than fish roasted in the oven.
Furthermore, like other low-temperature cooking methods, sous vide cooking may result in less hazardous HAs developing during the cooking process.
Which Method Should you Choose?
Fish is a nutritious item that may be included in any diet. However, the nutrition profile of your fish can be affected by the type of fish, cooking method, cooking time, and cooking oil you use. Overall, the healthiest cooking methods save the most nutrients and decrease the development of hazardous chemicals while limiting the loss of good omega-3 fats. Sous vide, microwaving, baking, steaming, and poaching your fish are your best bets. On the other hand, deep-frying is the least healthful Method of cooking fish.
Which is the Best Fish to Eat?
Fish, particularly oily fish such as salmon and tuna, are abundant in minerals and protein. Fish is a mainstay of the Mediterranean diet because it contains less cholesterol and saturated fat than beef. Vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins, zinc, and iron, are also found in fish.
How can you Tell When Fish is Done?
You should avoid overcooking many types of fish because they are delicate and tender. Testing your fish with a fork at an angle, at the thickest point, and gently twisting it is best to tell if it’s done. It will flake easily and lose its translucent or raw appearance when the fish is done.
Cooking the fish to an internal temperature of 140-145 degrees is a good rule. Try the 10-minute rule, which states that you should measure the thickness of the fish at its thickest point and cook it for 10 minutes per inch, turning halfway through.
What to Put on Fish?
- Parsley Sauce: This easy, lemony sauce is fantastic with crisp, butter-fried sea bass or snapper.
- Smoked-Almond Romesco Sauce: Smoked almonds and a touch of pimentón de la Vera gives this sauce a terrific smokiness.
- Fresh Herb Sauce: All you need for this sauce are parsley, arugula, marjoram, oregano, vinegar, and garlic.
- Rich Ketchup Sauce: Ketchup, soy sauce, vinegar, and Tabasco come together in this complexly flavored sauce.
- Mint Sauce: Fresh mint blends with garlic, vinegar, and sugar for a sweet-and-sour sauce perfect for a full-flavored fish like tuna.
- Lemon Cream Sauce: It doesn’t get much simpler than lemon zest, cream, salt, lemon juice, and parsley.
- Salmoriglio Sauce: This tangy, buttery sauce is a Sicilian classic.
- Red Wine Sauce: The success of this simple sauce lies in the quality of the wine. Choose a full-bodied red for a richly colored, flavorful sauce.
- Tomato Ginger Sauce: Though you can put this simple tomato sauce together in minutes, it has surprising complexity.
- Sweet-and-Sour Sauce: This healthy version of classic Chinese-takeout sweet-and-sour sauce is light and spicy.
Undercooked Fish
It may only pose a minor health risk to most healthy people who choose to eat raw or undercooked seafood, but the risk can be severe for others. Salmonella and Vibrio vulnificus are two common types of food poisoning caused by eating raw or undercooked fish and shellfish. If you insist on eating raw or partially cooked fish and shellfish, there are a few things to consider.
Parasites can be found in some fish species, and freezing them kills any parasites. Be aware; however, that freezing does not eliminate all harmful microorganisms. Undercooked fish is translucent and resists flaking. If your fish is undercooked, keep heating it until fully cooked. But keep in mind that fish cooks quickly, so keep an eye on it.
Conclusion
Fish is delicate and elegant, and it lends itself to a wide range of recipes. It’s an important ingredient to experiment with, whether in a fragrant fish curry or a crisp fried fry. Many people, however, avoid making it because they believe it to be difficult. While cooking fish does require some skill, it is relatively easy to learn. The first step in mastering any recipe or dish is to obtain the most incredible ingredients.
Fish should be cooked for ten minutes per inch of thickness in general. If you’re using paper, foil, or cooking in a sauce, add another five minutes. All options are boiling, broiled, fried, seared, grilled, steamed, poached, blackened, and acid-cooked fish. Naturally, health-conscious people should avoid fried foods, but all other methods provide a tasty and healthy alternative. Traditional, even ancient, methods of preparing fish exist in many cultures. They provide tried-and-true seasoning and preparation methods for various fish and are well worth investigating.