The cashew nut is native to Brazil and is farmed in Vietnam, Nigeria, India, and the Ivory Coast. The evergreen cashew tree (Anacardium occidentale) produces both a fruit (also known as an apple) and a nut (also known as a seed) that hangs beneath the fruit. Cashews are eaten as a snack on their own, in nut mixes, and as cashew butter, cashew milk, and other products. When used in moderation, cashews can be a nutritious supplement to your diet.
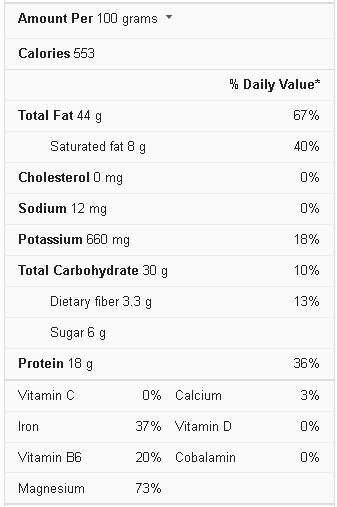
Cashews are nutrient-dense and widely consumed. A 100-gram serving of cashews contains 553 calories, 44 grams of fat, 18 grams of protein, and 6 grams of sugar.
Cashew Nut Nutrition Facts
What are Cashews?
Cashews are a nut with a soft texture and a sweet taste. They originated in South America, specifically Brazil, and were brought to Africa and India by colonists. These are the world’s largest cashew growers now. Raw or roasted cashews, salted or unsalted, are available. Cashew milk, cashew-based cheese, cashew-based cream sauces, and cashew-based sour cream were developed as dairy substitutes. This is one of a series of articles about the health advantages of common foods. It discusses the nutritional content of cashews and their potential health advantages. You’ll also discover how to incorporate cashews into your diet and learn about any potential health dangers.
What are the Health Benefits of Cashews Nuts?
Here are some health benefits of eating cashews nuts:
Aids Weight Control
If you’re attempting to lose weight, nuts are a good choice. Nuts contain nutritious fats, proteins, and fiber that can help you feel full and satisfied after meals or snacks. However, because nuts are high in calories, they should be used in moderation.
According to one study, routinely consuming nuts (about one handful daily) can be adopted as a component of a healthy diet to prevent obesity and type 2 diabetes over the long run.
However, the study looked into using nuts as a substitute for less healthful diets. The results of this study are inconclusive as to whether nuts give any unique benefits.
May help Decrease Cholesterol
According to a study published in the journal Nutrients in 2017, cashews may help decrease LDL cholesterol in some adults. When persons with mildly high cholesterol ingested 28 to 64 grams of cashews per day, their LDL cholesterol dropped by an average of 24 percent when compared to a control diet. According to the study authors, the fatty acid profiles, vegetable proteins, fibers, vitamins, minerals, carotenoids, and phytosterols in cashews and other nuts are responsible for the health advantages of nuts.
May Reduce Risk of Gallstones
There’s some evidence that consuming nuts help lower the risk of gallstones in both men and women.” Because of the richness of nuts in bioactive components, mainly unsaturated fatty acids, fiber, and minerals,” the authors of one comprehensive research review on nut benefits concluded, “a preventive impact of nut diet on gallstone disease is biologically conceivable.”
May Aid Diabetes Management or Prevention
Many researchers have looked into the link between nut consumption and diabetes. According to one study, nut consumption has been linked to a lower incidence of type 2 diabetes in women. Data from the major Nurses Health Study, the massive Iowa Women’s Health Study, the Physicians’ Health Study, and other published papers were summarized by the authors of an extensive research review. When women who ate nuts were monitored for lengthy periods, they were shown to have a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in some circumstances. However, not all data supported that conclusion, and the effect was only shown in women.
Promotes Better Heart Health
Cashews, like all nuts, are heavy in fat, but they contain poly and monounsaturated fats, which are heart-healthy fats that help lower cholesterol levels when ingested in moderation. Cashews are also high in dietary fiber, linked to a heart-healthy diet. Plant-based diets that incorporate healthy fats and protein from nuts and seeds (rather than meat products) have also improved heart health studies.
What are the Risks of Cashews?
Cashews include fat, but it’s unsaturated, mainly fat, and good for you in moderation. Raw cashews are dangerous to eat because they contain a substance called urushiol, found in poison ivy. Urushiol is poisonous, and some people may experience a skin reaction if they come into touch with it.
In supermarkets, cashew kernels are frequently offered as “raw,” but these have been steamed, and toxins are removed due to this process. These cashews are good for you.
Depending on the brand, salted and roasted cashews may have significant quantities of salt and fat, which may not be healthy. It’s best to read the label first and eat a tiny amount of these nuts. People with nut allergies should avoid cashews because they contain allergens that can cause severe reactions, including life-threatening anaphylactic shock. Overall, it is preferable to eat a varied diet rather than focusing on a single meal as the key to good health.
Varieties
There are no various types of cashews; however, there are several classes based on the nuts’ color, shape, and size. Only a few grades make it into stores where they can be purchased whole. Cashews are frequently found in canned nut mixtures in the grocery store’s snack food aisles. Nut blends and mixes may contain nuts that have been roasted in oil or seasoned with high salt or sweet substances. Check the nutrition information, as they will differ significantly from cashews alone.
Cashew Nut Butter
Cashew butter is a spread created from blended roasted cashews that some people appreciate. Peanut butter is a better option if you’re looking for a protein boost from nut butter. On the other hand, Cashew butter has a milder flavor than some people prefer.
The nutrients in your nut butter are ultimately determined by the ingredients added during preparation. Look for nut butter that is made entirely of nuts. Some may also have oil added to them. Avoid nut kinds of butter with added sweeteners or high sodium levels.
Cashew Milk
Cashew milk is also available and may be a good option for those who need to avoid lactose, which is present in dairy products. However, keep in mind that many nut milk, such as cashew milk, may have additional components such as added sugar and may not supply as many micronutrients (such as calcium) as dairy milk. Before you decide, make sure to read the nutrition facts label and the ingredients list on the nut milk you’re considering.
How to Prepare?
Raw or roasted cashews are both delicious. According to many individuals, they have a creamy, sweet texture that goes well with savory and salty dishes.
To add protein to a salad, sprinkle roasted or raw nuts on top, or top a small serving of ice cream with them. Chop them up and use them as a fish coating or toss them into your morning oatmeal.
The best way to store nuts is to keep them in an airtight container at room temperature. They should last around three months if stored properly. If you keep them in the refrigerator, they can last up to six months, and if you freeze them, they can last up to a year.
Amazon Brand Happy Belly Fancy Whole Cashews
Features:
- Happy Belly Fancy Whole Cashews have a delicate flavor and a firm texture for a rich, distinct taste
- Packaging might vary
- Premium whole Fancy grade cashews are roasted and salted with sea salt
- One 44-ounce stand-up, the resealable bag keeps cashews fresh
- Satisfaction Guarantee: We’re proud of our products. If you aren’t satisfied, we’ll refund you for any reason within a year of purchase. 1-877-485-0385
- An Amazon brand
Conclusion
Cashews are a good source of fiber, protein, and good fats. They also include a range of vitamins, minerals, and beneficial plant components that are good for one’s health. Cashews, like nuts, may help with weight loss, blood sugar regulation, and heart health. On the other hand, Cashews have received less research than other nuts. As a result, more research on cashews is needed to confirm these advantages.
However, there are drawbacks to including more cashews in your diet. Always choose unsalted dry-roasted or unroasted types if at all possible. Cashews are typically regarded as safe food. When possible, buy unroasted (sold as “raw”) unsalted cashews and soak them before eating to get the maximum advantages. The antioxidant activity of cashews is increased when they are dry roasted.