Spaghetti is a popular type of pasta used in a variety of dishes all over the world. Because durum wheat is used to make most spaghetti, it is high in complex carbohydrates and contains all the nutrients found in refined white flour. Regular spaghetti is relatively low in calories, but whole-wheat spaghetti is high in fiber. The amount of spaghetti and whatever you put on top of it determines whether or not your meal is healthy. To know spaghetti nutrition facts, read further.
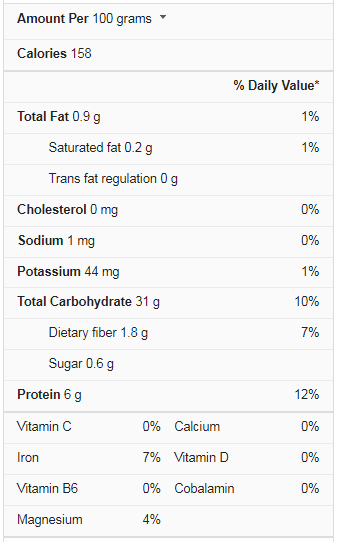
Spaghetti is high in carbohydrates, fiber, and other essential vitamins and minerals. To begin with, it contains no saturated fats or sodium. Protein, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium are present in significant amounts, and their nutritional value is enhanced when made with whole wheat. Let’s look at how these nutrients relate to the health benefits of spaghetti in more detail.
Spaghetti Nutrition Facts
What is Spaghetti?
Spaghetti is a cylindrical, long, thin, solid pasta, and it is an essential part of traditional Italian cuisine. Spaghetti, like other pasta, is made from milled wheat and water and is sometimes supplemented with vitamins and minerals. Durum wheat semolina is used to make Italian spaghetti. The pasta is usually white because refined flour is used, but whole wheat flour can be added. Spaghetti is divided into two types: thicker spaghetti and thinner capelin.
Spaghetti used to be very long, but in the latter half of the twentieth century, shorter lengths became more popular, and it is now most commonly available in 25–30 cm (10–12 in) lengths. It is used in various pasta dishes and is frequently served with tomato sauce, meat, or vegetables.
Important Facts
Let’s check out some exciting facts about spaghetti that you may have never heard of.
- Thin spaghetti is known as capelin.
- spaghetti is the thicker version of spaghetti.
- Usually, pasta is white because of the use of refined flour.
- It is primarily available in 25 to 30 cm (10 to 12 inches).
- Fresh spaghetti is made by rolling out pasta sheets and cutting them into strips with a rolling pin and a knife. The use of a pasta machine simplifies the process and makes it uniform.
- Fresh spaghetti can usually be cooked within a few hours of being manufactured.
- Dried spaghetti is made using auger extruders. Newly-made spaghetti is dried with proper moisture control to prevent the strands from sticking while ensuring it’s not too dry and brittle.
History of Spaghetti
The pasta was first mentioned in history in the 5th century when it was described as dried portable pasta that had to be cooked by boiling. Around the 12th century, it was transformed into long, thin forms in the west. Spaghetti became more well-known throughout Italy after spaghetti factories were established in the nineteenth century. This allowed for the mass production of spaghetti in Italy, spreading to restaurants in the United States. For decades, oregano and basil were not used in traditional spaghetti preparations. It is now widely used in various culinary preparations all over the world.
What are the Health Benefits of Spaghetti?
Pasta and spaghetti have traditionally been essential components of the Mediterranean diet. The benefits of spaghetti are now more widely available worldwide, making them more accessible to people everywhere. Let’s take a closer look at a few of the significant advantages of spaghetti.
Rich in Energy-boosting Carbohydrates
Spaghetti is primarily made with flour, high in carbohydrates, which are the body’s primary energy source. A spaghetti meal can thus provide that energy boost. A no-carb diet may deprive you of essential nutrients, even though some fad weight-loss diets advocate only the use of protein and fats. You can make it a wholesome meal by using whole wheat spaghetti and adding some lean meat protein or steamed vegetables.
Rich in Dietary Fiber
Whole wheat spaghetti is higher in fiber than regular pasta, and fiber keeps your blood sugar in check and your digestive system in good shape. Spaghetti is a quick and straightforward way to meet your daily carbohydrate needs, and Chickpea or zucchini spaghetti is a good option if you’re trying to avoid gluten.
Might be Good for your Heart
Mediterranean foods, such as spaghetti, may also help you maintain your cardiovascular health, and this is because it contains no cholesterol or saturated fats and is low in sodium. As serum cholesterol levels rise, plaques form inside blood vessels, causing a blockage (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, or ASCD) and stroke. A study of postmenopausal women found that replacing starchy foods with pasta meals reduced the risk of stroke and ASCD. Spaghetti, rather than other high-cholesterol, fat-laden foods, can be a good meal option if you avoid excessive amounts of salt, cheese, or butter in its preparation. Whole wheat spaghetti would be a better substitute than regular flour spaghetti.
Provides Protein and Micronutrients
One serving of spaghetti contains 6 grams of protein, which is approximately 16 percent of the RDA for adults. It also contains about 10% of your recommended daily allowance of iron, 5% of your recommended daily allowance of vitamin B-6, and 6% of your recommended daily allowance of magnesium. Proteins and micronutrients are essential for muscle growth, bone health, blood pressure regulation, and cancer and cardiovascular disease prevention.
Is Pasta Bad for your Health?
Allergies and Interaction of Spaghetti
Gluten-intolerant people should avoid spaghetti made with flour as the main ingredient. Gluten is a protein found in grains such as wheat, rye, and barley. While most people tolerate it well, those who are allergic to it may experience problems. Also, people with celiac disease should avoid regular pasta because gluten can trigger an immune response that damages small intestine cells. You can choose gluten-free spaghetti in these situations. Spaghetti has a long and illustrious history, and almost everyone enjoys it. If you’re new to spaghetti or want to improve your skills, here are some helpful hints and recipes.
How does Spaghetti Compare to Other Types of Pasta?
Pasta comes in various sizes and shapes, such as noodles, shells, macaroni, and so on. Some portions of pasta, such as spaghetti, are typically served with sauce, but other portions of pasta are frequently used as the main ingredient in soups and casseroles. Any pasta will have a similar nutritional value if the serving size is the same.
Does Pasta have Gluten?
Gluten, a protein found in grains like wheat and barley, is present in spaghetti because it is typically made from wheat. Gluten consumption is a problem for people who have celiac disease, wheat allergies, or intolerances, but the rest of us don’t need to avoid it. Some fad diets are based partly on avoiding gluten, but they aren’t backed up by scientific evidence. If you must avoid gluten, gluten-free pasta made from corn or rice is available. It has about the same number of calories as wheat pasta and is still high in carbohydrates. It’s also classified as a grain, and it’s no better or worse for you in terms of nutrition than regular pasta.
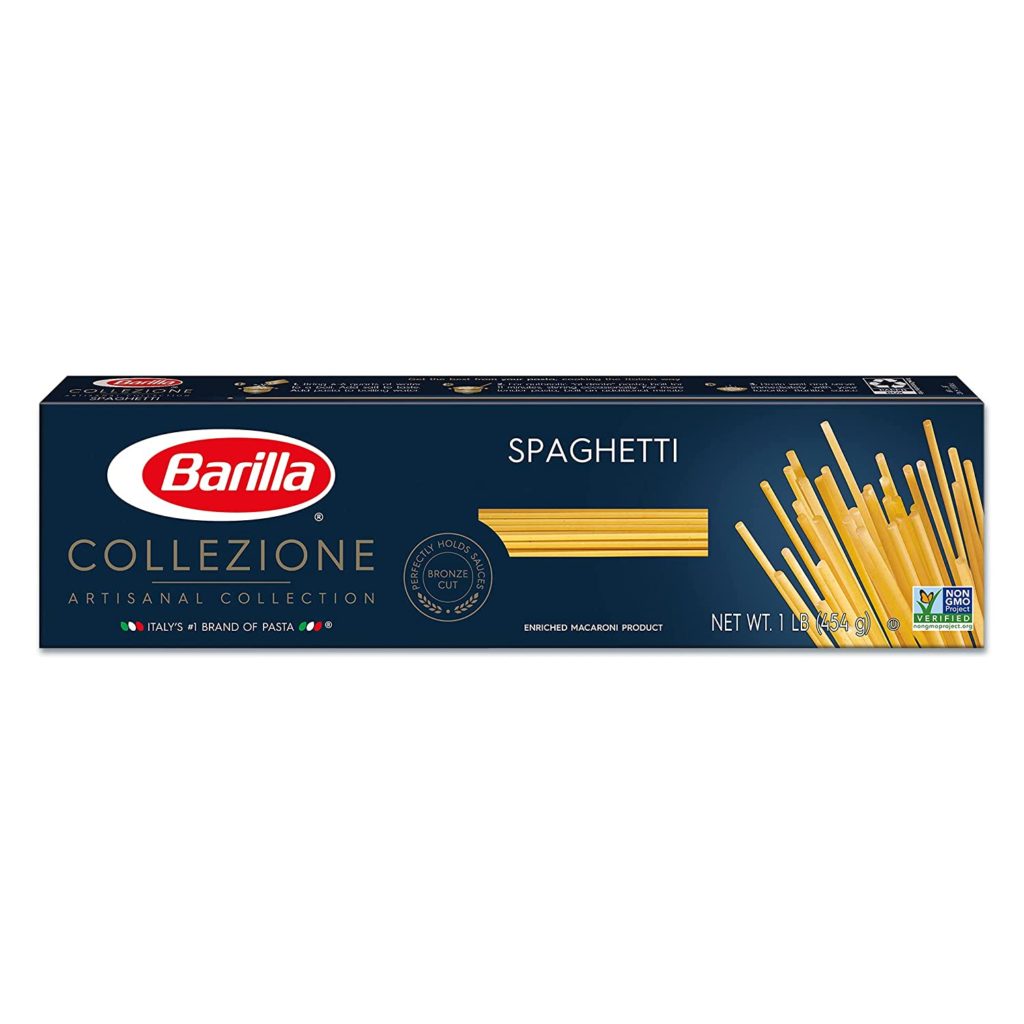
BARILLA Collision Spaghetti Pasta
Features:
- Create authentic Italian pasta dishes that are rich in flavor and imagination
- With a name meaning “guitar spaghetti,” this pasta is known for its distinctive square shape
- The shape is formed by pressing pasta dough through bronze dies to provide a texture similar to homemade pasta
- Pair with your favorite sauce for a hearty and delicious dinner
- Specialty pasta originating from the Abruzzi region of Italy
- Create authentic Italian pasta dishes that are rich in flavor and imagination
Conclusion
One cup of (100 g) spaghetti contains 6 grams of total protein, making it a low-fat food. Additional toppings, such as cheese and a variety of pasta dressings, can add fat, calories, and carbs to your plate.
Spaghetti noodles can be an excellent weight-loss option. It is fat-free and contains low sodium foods. It also contains beneficial vitamins and minerals, such as iron and vitamin C. Pasta is a staple of many cultures’ diets and contains some essential nutrients. Pasta, on the other hand, is high in carbohydrates. High-carbohydrate diets have increased blood sugar levels and adverse health effects.
As a result, it’s critical to control portion sizes and choose healthy pasta toppings like vegetables, healthy fats, and protein. Finally, when it comes to pasta, moderation is key. While you can eat it occasionally, it’s essential to combine it with other healthy foods and make sure it’s only one part of a balanced diet.