Eggplants, also known as aubergines, are nightshade plants that are used in a variety of dishes all over the world. Although they’re commonly mistaken for vegetables, they’re actually fruits because they come from a blooming plant and contain seeds. There are many different sizes and colours to choose from. While rich purple eggplants are the most frequent, they can also be red, green, or black.
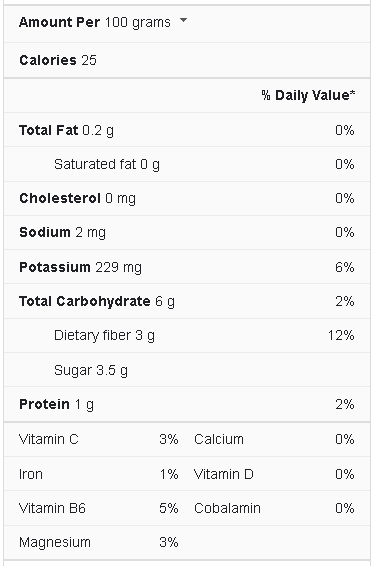
Eggplants’ vitamin, mineral, and nutritional richness are primarily responsible for their excellent health benefits. According to the USDA, eggplants are a good source of vitamin C, vitamin K, magnesium, phosphorus, copper, dietary fibre, folic acid, potassium, and manganese. They have a high water content with nearly little cholesterol or fat.
Like potatoes, tomatoes, and peppers, eggplant is a nightshade vegetable. It is native to India and Asia, where it can still be seen growing wild. They’re delicious on their own or in stews and curries. As a result, eggplants are not only a tasty addition to any meal, but they are also a nutritious supplement to any diet.
Eggplant Nutrition Facts
What Is Exactly Eggplant?
Eggplant (Solanum melongena) is a nightshade vegetable (technically a fruit). It’s also known as aubergine and comes in various hues and shapes. The presence of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals in eggplant contributes to its health advantages.
Consumption of eggplant can improve heart health, blood glucose regulation, cancer risk reduction, and cognitive performance. We’ve covered the health advantages of eggplant, its nutritional profile, strategies to incorporate it into your diet, and some of the concerns linked with it in this post. Continue reading! Eggplant has a thick, meaty inside that cooks down to creamy smoothness, and its substantial texture makes it a good meat substitute. For thousands of years, eggplant has been used in traditional medicine. White eggplant was used to treat diabetes, and the roots were used to treat asthma in the ancient Indian system of ayurvedic medicine.
Health Benefits of Eggplant
Eggplant has a lot of health benefits, and here are some of them:
High in Antioxidants
In addition to a wide range of vitamins and minerals. Antioxidants are chemicals that aid in protecting the organism against the detrimental effects of free radicals. Antioxidants have been demonstrated in studies to help prevent various chronic diseases, including heart disease and cancer. Anthocyanins, a pigment with antioxidant effects that gives eggplants their brilliant colour, are particularly abundant in eggplants. Nasunin, an anthocyanin found in eggplants, is particularly useful. In fact, several test-tube experiments have shown that it effectively protects cells from free radical damage.
May Reduce the Risk of Heart Disease
Some studies suggest that eggplants may help reduce the risk of heart disease due to their antioxidant content. In one study, rabbits with elevated cholesterol were given 0.3 ounces (10 ml) of eggplant juice twice a day for two weeks.
They had decreased levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides at the end of the trial, two blood markers that, when raised, can contribute to an increased risk of heart disease. Eggplants have also been shown to have a heart-protective impact in other research. Animals were fed raw or grilled eggplant for 30 days in one study, and both increased cardiac function and lowered the severity of heart attacks.
May Promote Blood Sugar Control
Including eggplants in your diet may help you maintain a healthy blood sugar level. This is due to eggplants’ high fibre content, which allows them to travel through the digestive system undamaged. Fibre can help lower blood sugar levels by reducing how sugar is digested and absorbed in the body. Slower absorption maintains blood sugar levels, avoiding spikes and crashes.
Other research suggests that polyphenols, or natural plant components, found in foods like eggplant may help lower blood sugar by reducing sugar absorption and increasing insulin secretion. Polyphenol-rich eggplant extracts were the subject of one test-tube investigation. It was discovered that lowering the quantities of particular enzymes that regulate sugar absorption could lower blood sugar levels.
May Have Cancer-fighting Benefits
Several chemicals found in eggplant have been shown to have anti-cancer properties. For example, Solasodine rhamnosyl glycosides (SRGs) are a type of chemical found in nightshade vegetables like eggplant.SRGs have been proven in animal studies to promote cancer cell death and may also help decrease the recurrence of certain types of cancer.
SRGs have been demonstrated to be particularly effective against skin cancer when administered directly to the skin, despite limited research on the subject. Furthermore, according to multiple studies, eating more fruits and vegetables, such as eggplant, has reduced the risk of some cancers.
Is Eggplant Good for Losing Weight?
Eggplants are high in fibre and low in calories, complementing any weight-loss diet. Fibre passes slowly through the digestive tract, promoting fullness and satiety while lowering calorie intake. Raw eggplant offers 3 grams of dietary fibre and only 23 calories per 100 grams. In addition, eggplants are frequently used in dishes as a high-fibre, low-calorie substitute for higher-calorie components.
Considering that eggplants are high in fibre and low in calories, they are a wonderful complement to any weight-loss strategy. Fibre passes slowly through the digestive tract and can increase feelings of fullness and satiety, which can help you eat less and lose weight. Raw eggplant contains 3 grammes of fibre and only 25 calories per cup of 100 grams of the vegetable.
While eggplant is not the most nutritionally dense vegetable available, it provides a good potassium and fibre source. And, with only 25 calories and less than 3 gramme of dietary fat per 100 grams serving, it’s a relatively guilt-free snack — as long as you don’t dunk it in oil before eating it.
Can You Eat Eggplant Raw?
Fortunately, the answer is a resounding yes! While the leaves and petals can be hazardous, the eggplant itself is safe to eat raw or cooked, and the chemical solanine, which some people are sensitive to, is only toxic in large doses.
To attain potentially hazardous levels of solanine, you’d have to eat more than a dozen full eggplants (at least!) in one sitting. (For further information on the topic, see Solanine in Sprouting Potatoes.) In fact, the chemical can be found in fried eggplant as well. Solanine is present in boiled eggplant. However, it is destroyed when the eggplant is fried.
When Should You Not Eat Eggplant?
If eggplant has gone bad, you should never eat it since the taste and fragrance will be unpleasant. If you observe any bruises on the flesh or breaks in the skin or peel, you should avoid eating eggplant. The flesh of eggplant over a year old will be less firm and may split from the peel.
Because eggplants are members of the nightshade family, they contain alkaloid solanine, which can be hazardous in high doses. Because substantial alkaloid levels are present in portions of the plant that are not ordinarily consumed, eating the leaves and tubers of nightshade plants can be lethal.
How to Eat Eggplant Raw?
If you’ve been debating whether or not to eat raw eggplant, you’ve probably noticed that there aren’t many recipes that call for it. While raw eggplant may be eaten without cooking, it has a bitter taste. Therefore it isn’t always at the top of dish makers’ lists. However, there are methods to lessen the bitterness or make it work in your favour.
To begin, select smaller eggplants or opt for Asian eggplant varieties such as Thai or Japanese eggplants, which are less bitter than the traditional purple-black kind found in your production area. Then, make careful you peel them because the peel contains a lot of bitterness. Finally, salt the peeled eggplants and drain them to eliminate some of the bitterness and extra water, which will improve the texture and flavour.
Conclusion
Raw eggplant is an underappreciated ingredient that can add taste and texture to several cuisines while also extending the meat component in some recipes. It’s also reasonably priced and high in nutritional value. Don’t be scared. If you’ve never had raw eggplant before, it’s worth a shot—stay away from the leaves and flowers, as they can be harmful.
Eggplant is a high-fibre, low-calorie meal packed with nutrients and many possible health advantages. Eggplants are an easy and delicious addition to any healthy diet, helping with heart disease prevention, blood sugar control, and weight loss. They’re also extremely adaptable and work well in a variety of meals.
The chemical solanine is found in eggplant and other nightshade plants, and some people believe it contributes to inflammation and makes conditions like arthritis worse. There’s no proof that the small quantity of solanine found in eggplant makes arthritic symptoms worse. However, if you discover that eating eggplant causes your joint discomfort to worsen, avoid it.