Whitefish, such as bass, is one of the most nutrient-dense foods available. It contains a high concentration of complete and highly bioavailable protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and selenium. It also has 124 calories per 3-ounce (100-gram) serving. The health benefits and nutrition facts are nearly identical whether you eat sea bass, striped bass, or any other type of bass.
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are omega-3 fatty acids found in small amounts in the bass (docosahexaenoic acid). The most important omega-3 fatty acids to get from your diet are EPA and DHA, and animal protein and algae are the most common sources. Cancer, cardiovascular disease, rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, ADHD, and other diseases are protected by EPA and DHA.
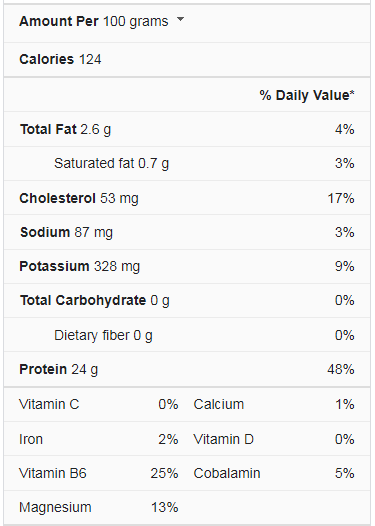
Sea Bass Nutrition Facts
What is Sea Bass?
Sea bass is small fish that live between Florida and Cape Cod in the western Atlantic. Unlike other bass species such as striped bass and white bass, Sea bass can only be found in the ocean. Several “bass” species, such as Chilean sea bass, are fish renamed to increase marketability. The sea bass, also known as black sea bass or blackfish, is a large bottom feeder with a grayish-black body and a white belly. The flesh is white and firm, with small, tight flakes and a mild flavor.
They are usually sold whole, weighing 1 1/2 to 2 pounds, and are occasionally sold alive at Asian markets. Fish with a deep color, bright eyes, and pink (not brown) gills should be avoided. Steamed or roasted whole sea bass is delicious (Try it with Asian seasonings). Fillets are commonly baked in parchment paper or foil packets and can be sautéed or broiled. Fried whole fish and fillets are both delicious.
Varieties
Bass are found in both freshwater and saltwater and come in various species. The majority of what you’ll find in local markets comes from saltwater. Striped bass, sea bass, and white bass are the most common bass species. Bass flesh is typically white, delicate, and flaky. However, the flavor will vary depending on the bass you eat.
What are the Health Benefits of Sea Bass?
Bass supports the immune system, prevents B12 deficiency, and helps with anxiety and depression, among other things. Here are some of the health advantages of bass.
Helps Preserve Muscle Mass
Bass is a low-calorie food that is also high in quality protein, making it ideal for weight loss. A high-protein diet promotes muscle growth and preservation while also increasing satiety.
Promotes Satiety
One review of data published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that higher-protein diets improved body weight, appetite control, and cardiometabolic risk factors.
Provides Immune System Support
Selenium is a trace mineral that functions as an antioxidant in the human body. This micronutrient has several health benefits, including improving immune function. A diet high in selenium will aid in the development of a barrier against infections and illnesses such as the cold and flu. In addition, selenium helps immune cells fight off invading organisms and free radicals. To improve the function of your immune system, you should eat foods high in selenium.
Helps Prevent Anemia
Vitamin B12 is a micronutrient that can only be obtained through food. Animal products, such as meat, fish, dairy, and eggs, are high in B12. You’re more likely to develop vitamin B12 anemia if you don’t get enough B12 in your diet. Anemia occurs when your body lacks enough red blood cells to transport oxygen where it is needed, and this causes weakness and exhaustion. Infertility, heart conditions, nervous system problems, congenital disabilities, pregnancy complications, and even heart failure may occur if left untreated.
The majority of people have no trouble getting enough vitamin B12. However, if you follow a vegan diet that excludes animal products, it cannot be easy to meet daily B12 requirements. A supplement may also be beneficial if you take medication or have a pre-existing condition that prevents B12 absorption.
Improves Heart Health
In the United States, heart attack and stroke remain the leading causes of death. A diet high in omega-3-rich foods, such as bass, has been shown to improve heart health. These advantages include lower blood triglycerides, lower LDL (bad cholesterol) levels, and higher “good” HDL cholesterol levels. Omega-3 fatty acids have also improved heart health by lowering inflammation and blood pressure.
Offers High-Quality Protein Source
One of the leanest protein sources available is bass. Every 3-ounce cooked portion provides 20 grams of high-quality protein or about 6 grams of protein per ounce. Bass is also a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids and is high in leucine, the amino acid responsible for muscle growth and preservation.
Negative Consequences
Mercury levels are high in all varieties of bass. Because of the high mercury content, pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children should avoid eating bass or choosing a different type of fish. Potassium is abundant in the bass. Those with kidney disease should avoid bass or consult a doctor before incorporating it into their diet.
Is Bass Healthier than Salmon?
Salmon contains more omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, potassium, calcium, and zinc than sea bass, making it healthier. The FDA recommends eating sea bass only once or twice a week because it contains more mercury than salmon, and salmon is safe to eat two to three times per week.Sea bass contains, a wide variety of minerals and vitamins, though not as much as salmon. Sea bass has fewer calories and fat and more magnesium, and they both have the same amount of selenium and phosphorus.
The high amount of heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids in salmon is the first and most important reason it outperforms most fish. These omega-3 fatty acids aid in the prevention of heart attacks, strokes, hypertension, and other heart-related problems. This is due to omega-3s’ ability to keep arteries strong and healthy while keeping lousy cholesterol in check. Believe it or not, Salmon is also good for your hair, nails, and skin, and it can help with the metabolism of your hair and nails.
Furthermore, the antioxidants in salmon meat can help keep free radicals at bay, leading to heart disease and cancer. Like much other fish, Salmon is high in vitamins, particularly vitamin B. These vitamins are critical for maintaining the health of your heart and blood vessels.
Salmon also contains selenium, a mineral that helps to maintain the health of your hair and nails.
Salmon, on the other hand, does not contain any cancer-causing compounds. Many types of red meat contain carcinogenic elements that, if consumed, can be harmful to your health. Fortunately, with salmon, you won’t have to worry about that. The only thing you should avoid (which applies to both seabass and salmon) is overeating it. Yes, salmon is a healthy food that can benefit your body, but there is such a thing as too much of a good thing.
How to Prepare?
Bass cooks quickly and easily, with little seasoning required. Pan-fried, baked, broiled, poached, grilled, or cooked in a soup or stew are all options.
Dry the fillet with a paper towel before pan-frying it. Lightly season both sides with salt and pepper. Once the pan is hot, add a small pat of butter or olive oil and cook the fish over medium-high heat.
Allow 4 minutes for the fish to cook. Gently flip the fish over with a spatula and cook for an additional 3 to 4 minutes, or until the fish is cooked through and flaky. Serve immediately with a squeeze of lemon on top.
Storage and Food Safety
Fresh bass can be kept in an airtight container in the refrigerator for two days. Raw fish can be frozen for up to 3 months if tightly wrapped in plastic wrap, while cooked fish can be kept in an airtight container in the refrigerator for four days. Cooked fish can be frozen for up to 3 months in an airtight container.
Fresh or raw fish should be discarded if left out at room temperature for more than 2 hours or has developed an odor. If it’s a hot day or the temperature where it was left out is above 90 degrees Fahrenheit, the time range is reduced.
Can I Eat Fish Every Day?
It is not recommended to eat fish every day. Because it’s assumed that you also eat chicken and beef, too much protein won’t allow you to reap the full benefits.
When you eat chicken and beef, eating fish once or twice a week is recommended. Take a serving of fewer than 6 ounces if you eat the principal meal of the day. Fish can be prepared by grilling, grilling, or boiling.
Avoid using it in fast food items like chips, fish sandwiches, or deep frying. Because of the complex processing, which is high in bad fats, the nutrition will change. According to one study, fried fish and fish sandwiches do not provide any cardiovascular benefits.
Conclusion
Seabass contains 6 to 11 percent of your daily magnesium and potassium requirements. They’re high in selenium, which your body needs for antioxidant production and thyroid hormone synthesis. According to Thompson’s Seafood, Sea bass is a good source of vitamin B-6.
Thompson’s seafood, based in Tottenham, knows that one serving of sea or freshwater bass is low in calories and high in protein, selenium, and essential omega-3 fatty acids. Both sea and freshwater bass have the same nutrients but different amounts, such as B-12 and B-6 vitamins. The only disadvantage of bass is mercury, which pregnant women and children should avoid.