Trout is a ray-finned, tender fish in the salmon family, and white, pink, or orange flesh can be found. Trout has a mild flavour, which is excellent news for those who dislike fishy seafood. This popular fish abounds in protein, healthy fats, vitamins like vitamin D, and minerals. Fish is high in omega-3 fatty acids: EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), both of which are good for our hearts.
Baked, broiled, grilled, smoked, pan-fried, sauteed, or steamed trout are all options. It goes well with asparagus, red potatoes, rice, or a green salad as a side dish. Everything you need to know about trout nutrition, health benefits, preparation, and storage is here.
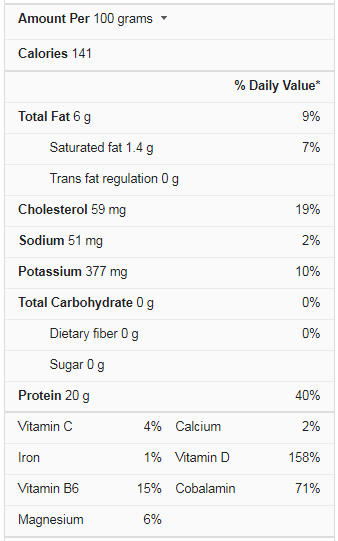
Trout Nutrition Facts
What is Trout?
Trout are freshwater fish that belong to the genera Oncorhynchus, Salmo, and Salvelinus, which are all members of the Salmonidae subfamily of the Salmonidae family. Some non-salmonid fish, such as Cynoscion nebulosus, the spotted seatrout, or speckled trout, have the word trout in their name.
Salmon and char (or charr) are closely related to trout: salmon and char species are found in the same genera as trout (Oncorhynchus – Pacific salmon and trout, Salmo – Atlantic salmon various trout, Salvelinus – char and trout).
Lake trout and most other trout live exclusively in freshwater lakes and rivers. In contrast, others, such as steelhead, a type of coastal trout, can spend up to three years at sea before returning to spawn in freshwater (a habit more typical of salmon). The char genus includes Arctic char and brook trout. Trout are an essential food source for humans and wildlife, including brown bears, eagles, and other birds of prey. Oily fish is what they are called.
What are the Health Benefits of Trout?
In addition to being a lean white fish, Trout has numerous health benefits for pregnant women and their brains, heart, and bones. Here are some of the health benefits of trout.
Great Source of Protein
Muscles, bones, skin, blood, and cartilage require protein. While the amount of protein you require each day is dependent on several factors, such as your weight and level of activity, aiming for the minimum requirements of 46 to 56 grams per day is ideal.
Including trout at least twice a week in your diet can help you meet your protein requirements. Furthermore, if you’re trying to lose weight, choosing a lean protein source like fish over fatty red meats can help you consume fewer calories.
Heart-Healthy Fats
Trout is high in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial to both healthy and cardiovascular disease patients. Omega-3 fatty acids can lower triglyceride levels while lowering blood pressure, preventing plaque from clogging arteries, and preventing arrhythmias.
Brain-Boosting Fats During Pregnancy
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and heart health, and Omega-3 fatty acids help your fetus develop a healthy brain during pregnancy. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), pregnant women should eat at least two servings of fish per week during pregnancy and breastfeeding to benefit from the omega-3s in fish.
ACOG claims that “Mercury levels in some fish are higher than others, and mercury is associated with congenital disabilities. Bigeye tuna, king mackerel, marlin, orange roughy, shark, swordfish, and tilefish are all off-limits. Only eat 6 ounces of white (albacore) tuna per week. Check for advisories about fish caught in local waters as well.”
Excellent Source of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin required for bone development and remodelling, and it also aids calcium absorption, reduces body inflammation, and improves neuromuscular and immune function. Because vitamin D is found naturally in only a few foods, including trout in your diet is an excellent way to get a healthy dose of vitamin D. A 3-ounce serving of trout contains about 645 IUs of vitamin D or 81 percent of the daily value.
Allergies
Any food can cause an allergy to develop at any age. Hives, shortness of breath, wheezing, vomiting or stomach cramps, swelling of the tongue, dizziness, and, in rare cases, anaphylaxis is all common symptoms of food allergies. If you suspect a trout allergy, stop eating it and consult your doctor.
Storage and Food Safety
Only buy refrigerated fish or displayed on ice at the store or market. Store fresh trout in the refrigerator or freezer once you get home. Please place it in an airtight container after wrapping it in plastic or foil. You can keep your trout in the refrigerator if you plan to eat it within two days of purchase. Otherwise, wrap the trout tightly in plastic wrap and place it in an airtight container or freezer-safe bag before freezing. Remove the frozen trout from the freezer and thaw it overnight in the refrigerator before cooking. Thaw at room temperature only.
Is Trout a Superfood?
Rout is a superfood because it is high in nutrients. One serving provides a third of your daily protein, half of your Vitamin B-12, and all of your Vitamin D. Trout, like salmon, is high in omega-3 fatty acids, good for your heart. Protein is the foundation of our bodies. It aids in repairing damaged tissues and aids in growth and development. Mega 3 fatty acids are essential for brain function because they help with memory, performance, and behaviour, as well as average growth and development. Omega 3 fatty acids have also been shown to reduce inflammation and may help reduce your risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and arthritis.
Is Trout Healthier than Tuna?
For a quick recap of significant nutrients and differences between canned tuna and trout:
- Both canned tuna and trout are high in calories, potassium, and protein.
- Canned tuna has 64% less saturated fat than trout, and
- Trout has more thiamin, riboflavin, folate, and Vitamin B12. However, canned tuna contains more pantothenic acid.
- Trout has significantly more Vitamin A than canned tuna, and
- Trout has significantly more Vitamin D than canned tuna.
Is Trout Similar to Salmon?
While trout and salmon have a similar appearance and flavour, they are two different fish species. Salmon is a saltwater fish, whereas Trout is a freshwater fish. Salmon has a higher fat content and is almost always more significant in size than trout.
Salmon is healthier than trout because it contains nearly twice as many omega-3 fatty acids as trout, and salmon also has higher levels of vitamins C and B-6. However, both types of fish are healthy and recommended by the American Dietary Guidelines.
Buying Tips
Trout are available fresh or frozen, whole, trimmed, fileted, and occasionally steaks. Smoked, salt-cured, and canned varieties are also available. Purchase high-quality fish from reputable vendors. Purchase a whole trout side or a fillet from the fish’s thickest cut. The flesh of wild-caught trout will be pinker and brighter than that of farmed trout. Wild fish are nutritionally superior to farmed fish and contain fewer toxins. Artificial colourants/dyes have been reported in farmed trout to make them look like pink, wild trout.
In the markets, you can find ready-to-cook pâté, kabobs, marinated and peppered trout steaks, fillets, salted trout, and burgers similar to salmon. Avoid trout fish with a strong amine odour, just as with salmon. Smoked trout with leaky or wet edges should be avoided. Trout spoils quickly due to its fatty flesh, which attracts bacteria. Fish fillets and sections should always be kept in a deep freezer.
Conclusion
Trout do not have the same popularity as their salmon relatives. However, it provides a lot in terms of nutrition. Trout is high in omega-3 fatty acids, protein, vitamins, and minerals, for starters. Another advantage of trout is that it is much less expensive than salmon. Overall, this fish is a nutritious, affordable, and healthy addition to any diet.
Lemon, pepper, olive oil, garlic, dill weed, thyme, and a variety of other seasonings can enhance trout’s flavour. If you have any leftover rainbow trout, wrap it up and store it in the fridge, and it should not be left at room temperature.